Think about you might be launching a brand new digital service: you want to rapidly confirm the authenticity of buyer paperwork, securely retailer knowledge, and automate settlements with companions in several nations. An error in these processes can price an organization tens of millions, and a gradual system will drive prospects away.
That’s the reason enterprise homeowners are more and more turning their consideration to Distributed Ledger Applied sciences (DLT).
In response to Statista, the worldwide DLT market will exceed $127 billion by 2030 — a rise of greater than $100 billion in comparison with 2020. The primary driver is provide chain audits, which is able to attain $103 billion by the tip of the last decade, however different areas are additionally actively creating: digital identification, good contracts, and immutable data.
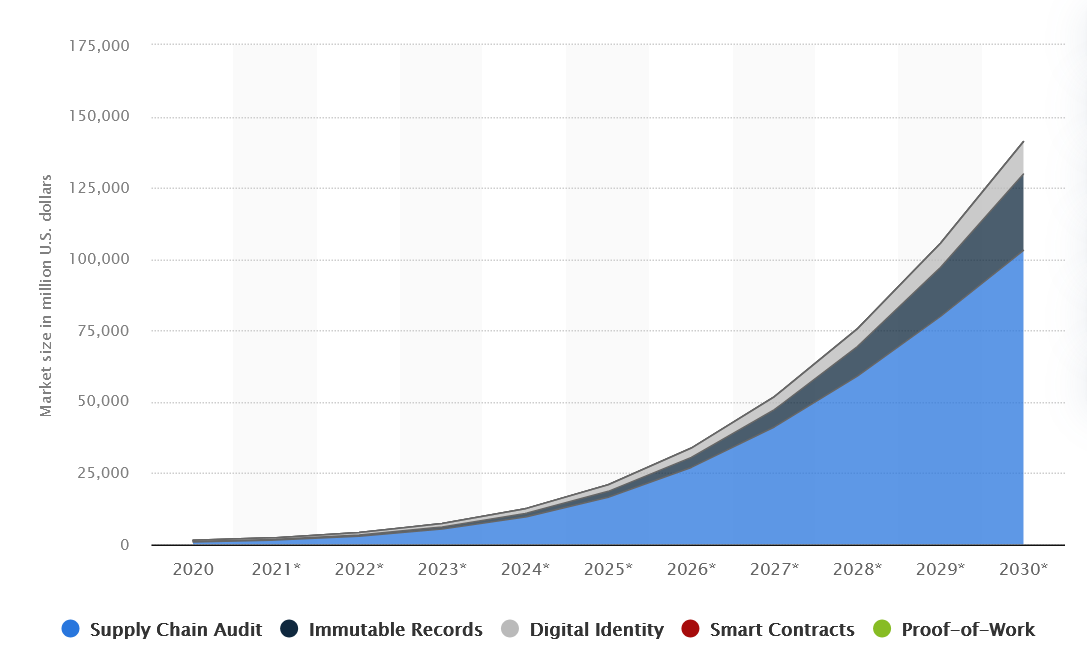
Distributed ledger market measurement worldwide from 2020 to 2030
Amid this fast growth, the query of “hashgraph vs blockchain” has turn into a key consideration for companies and builders exploring distributed ledger applied sciences.
On the one hand, blockchain has turn into the muse for tasks reminiscent of Bitcoin and Ethereum, proving that decentralization can efficiently work in actual enterprise.
Then again, hashgraph affords a distinct path: larger transaction velocity, energy-efficient consensus, and new alternatives for enterprise options.
For corporations, that is not a query of “know-how for know-how’s sake.” It’s a strategic alternative: on which platform to construct digital merchandise and enterprise providers so as to stay aggressive tomorrow.
Fundamentals of Distributed Ledger Applied sciences (DLT)
At this time, many corporations are contemplating implementing digital options the place belief in knowledge performs a key function.

Think about a state of affairs: a number of companions from totally different nations are engaged on one challenge, and every of them must make certain that the data of transactions or paperwork are correct and can’t be tampered with.
In conventional techniques, this belief is supplied by a single central authority — a financial institution, a authorities company, or a service supplier. However what if there is no such thing as a heart?
Distributed ledger applied sciences step in right here, serving because the spine for improvements like blockchain and hashgraph, and more and more changing into a subject of energetic dialogue within the enterprise world.
What Is DLT?
Distributed Ledger Applied sciences (DLT) are a approach of concurrently storing and synchronizing knowledge throughout all members in a community. As a substitute of counting on a single server, data is copied and up to date throughout a number of nodes on the similar time.
The important thing distinction is easy. A centralized system is dependent upon one operator. If that operator goes down, everybody feels the affect. With DLT, the info is unfold out, so each participant sees the identical model of occasions. This makes the system extra clear and far more durable to interrupt.
Due to this, corporations can construct providers the place members belief the info with out having to belief one another immediately.
The primary real-world purposes of distributed ledgers have been made doable by the arrival of blockchain, which first gained consideration by cryptocurrencies. In 2009, Bitcoin confirmed that worth might be exchanged immediately between people with out counting on banks or intermediaries.
A number of years later, Ethereum expanded the idea of blockchain by introducing good contracts — self-executing applications that routinely perform agreements. These improvements pushed blockchain far past the crypto group and paved the best way for a variety of enterprise purposes.
Hashgraph as a New Kind of DLT
If blockchain was the primary mass type of DLT, then hashgraph know-how is positioned as its improvement.
Not like a linear chain of blocks, hashgraph makes use of the construction of a directed acyclic graph (DAG), the place transactions are recorded not one after the other, however in parallel. This permits processing hundreds of transactions per second with minimal prices.
The primary variations from conventional blockchain are:
- Pace — hashgraph can deal with as much as 10,000 transactions per second, whereas Bitcoin is restricted to about 7 and Ethereum to round 30 (these numbers are for public blockchains; non-public ones can course of as much as 2,000 transactions per second).
- Vitality effectivity — due to the digital voting mechanism and gossip protocol, the community doesn’t require resource-intensive computations like PoW.
- Transaction finality — confirmations happen immediately, with out the necessity to look ahead to a number of blocks.
Variations Between Hashgraph and Blockchain
To know the variations between blockchain and hashgraph, it is very important analyze how they work. At first look, each applied sciences fall underneath DLT and remedy an identical drawback — storing and verifying knowledge in a decentralized community. Nonetheless, their mechanisms and structure differ considerably.
How Does Blockchain Work?
In blockchain, knowledge is grouped into blocks which might be related into a series. Every new block is linked to the earlier one, and altering an outdated file with out altering all the chain is virtually unattainable.
The community is maintained by nodes (computer systems) that validate transactions and retailer similar copies of the database. Blockchain additionally helps good contracts — small applications that routinely execute the phrases of an settlement.
To determine which transactions are legitimate, the community makes use of a consensus mechanism. The preferred choices are:
- Proof-of-Work (PoW) — utilized in Bitcoin, the place miners remedy puzzles so as to add a block (dependable, however very energy-intensive).
- Proof-of-Stake (PoS) — for instance, in Ethereum: new blocks are validated by members who’ve staked their cryptocurrency. This technique is quicker and extra resource-efficient.
How Does Hashgraph Work?
Hashgraph works in another way. There isn’t a chain of blocks. As we said above, it makes use of a construction referred to as a DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph), the place transactions are recorded in parallel somewhat than one after the other, which supplies the community higher velocity.
Info in hashgraph spreads by the gossip-about-gossip technique: every node shares what it is aware of with others, and on this approach, knowledge rapidly propagates throughout all the community.
On this foundation, digital voting is used: nodes don’t have to vote; they will merely calculate the consequence, since all of them have the identical data. That is the hashgraph consensus — a quick, honest, and safe approach to agree on the validity of transactions.
Hashgraph vs Blockchain: Detailed Comparability
For companies, choosing the proper blockchain community or various DLT like Hedera Hashgraph is a strategic determination.
We’ve already checked out how blockchain and hashgraph work, however for companies, it is very important see the clear variations in figures and traits. The desk under supplies a side-by-side comparability of each applied sciences throughout key parameters — from structure to efficiency.
| Criterion | Blockchain | Hashgraph (Hedera) |
| Structure | Linear chain of blocks. Every transaction is added sequentially. | Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG). Transactions are recorded in parallel. |
| Throughput | Restricted: Bitcoin ~7 TPS, Ethereum ~30 TPS (for public blockchains). | Excessive: as much as 10,000+ TPS within the Hedera Hashgraph community. |
| Transaction price | May be excessive underneath load: from just a few cents to tens of {dollars} (for public blockchains). | Very low: fractions of a cent per transaction. |
| Consensus algorithm | Proof-of-Work (energy-intensive) or Proof-of-Stake (more cost effective however complicated to handle). | Hashgraph consensus primarily based on gossip-about-gossip and digital voting. |
| Vitality effectivity | Low in PoW (large mining prices), larger in PoS. | Very excessive: no heavy computations, solely data trade. |
| Safety | Weak to 51% assault: an attacker with majority energy can rewrite historical past. | Asynchronous Byzantine Fault Tolerance (ABFT). The community stays sincere even when some nodes fail. |
| Finality | Requires ready for a number of blocks (in public blockchains): in Bitcoin — as much as 60 minutes. | Prompt finality — transactions are confirmed immediately. |
| Scalability | Restricted: larger load = larger charges and slower confirmations. | Excessive: designed for enterprise-level efficiency. |
| Use circumstances | Bitcoin, Ethereum, DeFi, NFT, provide chain (business-specific options for non-public blockchains can be found). | Hedera Hashgraph: micropayments, digital identification, enterprise purposes. |
Hashgraph vs Blockchain
Overview of Hedera Hashgraph
When individuals speak about hashgraph, they often imply its most well-known implementation — the Hedera Hashgraph platform. This community turned one of many first sensible makes an attempt to show DAG know-how and hashgraph consensus right into a working ecosystem obtainable to corporations and customers worldwide.
What Is the Hedera Hashgraph Platform?
Hedera Hashgraph is a public community designed to provide companies and builders a quick, safe, and scalable approach to make use of distributed ledgers. Not like many blockchains, Hedera will not be constructed round cryptocurrency as its core worth. As a substitute, it supplies a platform for creating purposes — from micropayments to digital identification techniques.
Key options:
- Excessive efficiency: hundreds of transactions per second with low charges.
- Transparency and belief: all members have equal entry to knowledge.
- Vitality effectivity: no pricey mining, in contrast to blockchain.
The community is ruled by the Hedera Governing Council — a board that features main international corporations (Google, IBM, Boeing, and others). This strategy builds belief with companies, since selections are made not by a single operator however by a bunch of impartial members.
Hedera Hashgraph and Blockchain: Competitors or Coexistence?
Many corporations wonder if Hedera Hashgraph can change present blockchain options or a minimum of combine with them. In follow, it’s extra about coexistence than competitors.
Hedera doesn’t set itself towards blockchain however somewhat enhances the DLT ecosystem. It may be used as a standalone platform or alongside different applied sciences. For instance, hashgraph is right for micropayments, high-throughput purposes, or IoT, whereas blockchain retains its sturdy place in cryptocurrencies, DeFi, and NFTs due to its mature infrastructure and broad ecosystem.
By way of strengths:
- Hashgraph wins the place velocity, scalability, low transaction price, and on the spot finality are important.
- Blockchain stays indispensable the place market belief and ecosystem maturity matter most — cryptocurrencies, DeFi, NFTs, and large-scale public tasks.
Thus, within the coming years, companies ought to focus not on selecting “either-or” however on hybrid architectures the place blockchain and hashgraph are utilized collectively, relying on the duty.
Way forward for DLT: Can Hashgraph Change Blockchain?
At this time, it’s troublesome to call a transparent winner within the debate between blockchain and hashgraph. On the one hand, blockchain has already confirmed its worth: it has turn into the muse for the biggest cryptocurrencies, hundreds of tasks are constructed on it, and traders proceed to pour billions into its ecosystem.
Then again, hashgraph is regularly attracting market consideration, particularly by the Hedera Hashgraph community, which is supported by main international firms. Its velocity, power effectivity, and dependable consensus make the know-how interesting for enterprise options.
In response to analysts, the DLT market will develop to lots of of billions of {dollars} by 2030, and each blockchain and hashgraph will share on this development. It’s unlikely that one know-how will utterly change the opposite.
SCAND and Distributed Ledger Applied sciences Improvement
At SCAND, now we have in depth expertise in creating options primarily based on blockchain applied sciences — from good contracts and crypto wallets to decentralized purposes (DAO, DeFi, NFT, and Web3). We assist corporations leverage distributed ledgers to enhance transparency, safety, and automation of enterprise processes.
Recently, now we have been actively exploring the potential of the Hedera Hashgraph community. This know-how opens new alternatives for enterprise options due to its excessive transaction velocity, power effectivity, and on the spot finality.
Why select us:
- We’ve deep experience in good contract improvement, blockchain improvement, and work with varied DLT platforms.
- We ship customized options tailor-made to particular enterprise wants — whether or not it’s cost techniques, digital identification, provide chain administration, or micropayments.
We see ourselves not simply as builders however as a companion who helps combine fashionable DLT options and unlock their potential for enterprise development and competitiveness.



