Evaluating OCR techniques that convert PDFs or doc pictures into Markdown is much extra advanced than it seems. In contrast to plain textual content OCR, OCR-to-Markdown requires fashions to get well content material, structure, studying order, and illustration decisions concurrently. At this time’s benchmarks try to attain this with a mixture of string matching, heuristic alignment, and format-specific guidelines—however in observe, these approaches routinely misclassify appropriate outputs as failures.
This submit outlines why OCR-to-Markdown analysis is inherently underspecified, examines widespread analysis methods and their failure modes, highlights concrete points noticed in two broadly used benchmarks, and explains why LLM-as-judge is at present essentially the most sensible technique to consider these techniques—regardless of its imperfections .
Why OCR-to-Markdown Is Laborious to Consider
At its core, OCR-to-Markdown doesn’t have a single appropriate output.
A number of outputs could be equally legitimate:
- Multi-column layouts could be linearized in numerous studying orders.
- Equations could be represented utilizing LaTeX, Unicode, HTML, or hybrids.
- Headers, footers, watermarks, and marginal textual content could or might not be thought of “content material” relying on activity intent.
- Spacing, punctuation, and Unicode normalization typically differ with out affecting that means.
From a human or downstream-system perspective, these outputs are equal. From a benchmark’s perspective, they typically usually are not.
Widespread Analysis Methods and Their Limitations
1. String-Based mostly Metrics (Edit Distance, Actual Match)
Most OCR-to-Markdown benchmarks depend on normalized string comparability or edit distance.
Limitations
- Markdown is handled as a flat character sequence, ignoring construction.
- Minor formatting variations produce massive penalties.
- Structurally incorrect outputs can rating properly if textual content overlaps.
- Scores correlate poorly with human judgment.
These metrics reward formatting compliance slightly than correctness.
2. Order-Delicate Block Matching
Some benchmarks section paperwork into blocks and rating ordering and proximity.
Limitations
- Legitimate different studying orders (e.g., multi-column paperwork) are penalized.
- Small footer or marginal textual content can break strict ordering constraints.
- Matching heuristics degrade quickly as structure complexity will increase.
Right content material is commonly marked unsuitable because of ordering assumptions.
3. Equation Matching by way of LaTeX Normalization
Math-heavy benchmarks usually count on equations to be rendered as full LaTeX.
Limitations
- Unicode or partially rendered equations are penalized.
- Equal LaTeX expressions utilizing completely different macros fail to match.
- Blended LaTeX/Markdown/HTML representations usually are not dealt with.
- Rendering-correct equations nonetheless fail string-level checks.
This conflates illustration selection with mathematical correctness.
4. Format-Particular Assumptions
Benchmarks implicitly encode a most popular output model.
Limitations
- HTML tags (e.g.,
) trigger matching failures. - Unicode symbols (e.g.,
km²) are penalized towards LaTeX equivalents. - Spacing and punctuation inconsistencies in floor reality amplify errors.
Fashions aligned to benchmark formatting outperform extra normal OCR techniques.
Points Noticed in Current Benchmarks
Benchmark A: olmOCRBench
Handbook inspection reveals that a number of subsets embed implicit content material omission guidelines:
- Headers, footers, and watermarks which are visibly current in paperwork are explicitly marked as absent in floor reality.
- Fashions skilled to extract all seen textual content are penalized for being appropriate.
- These subsets successfully consider selective suppression, not OCR high quality.
Moreover:
- Math-heavy subsets fail when equations usually are not totally normalized LaTeX.
- Right predictions are penalized because of illustration variations.
Because of this, scores strongly rely on whether or not a mannequin’s output philosophy matches the benchmark’s hidden assumptions.
Instance 1
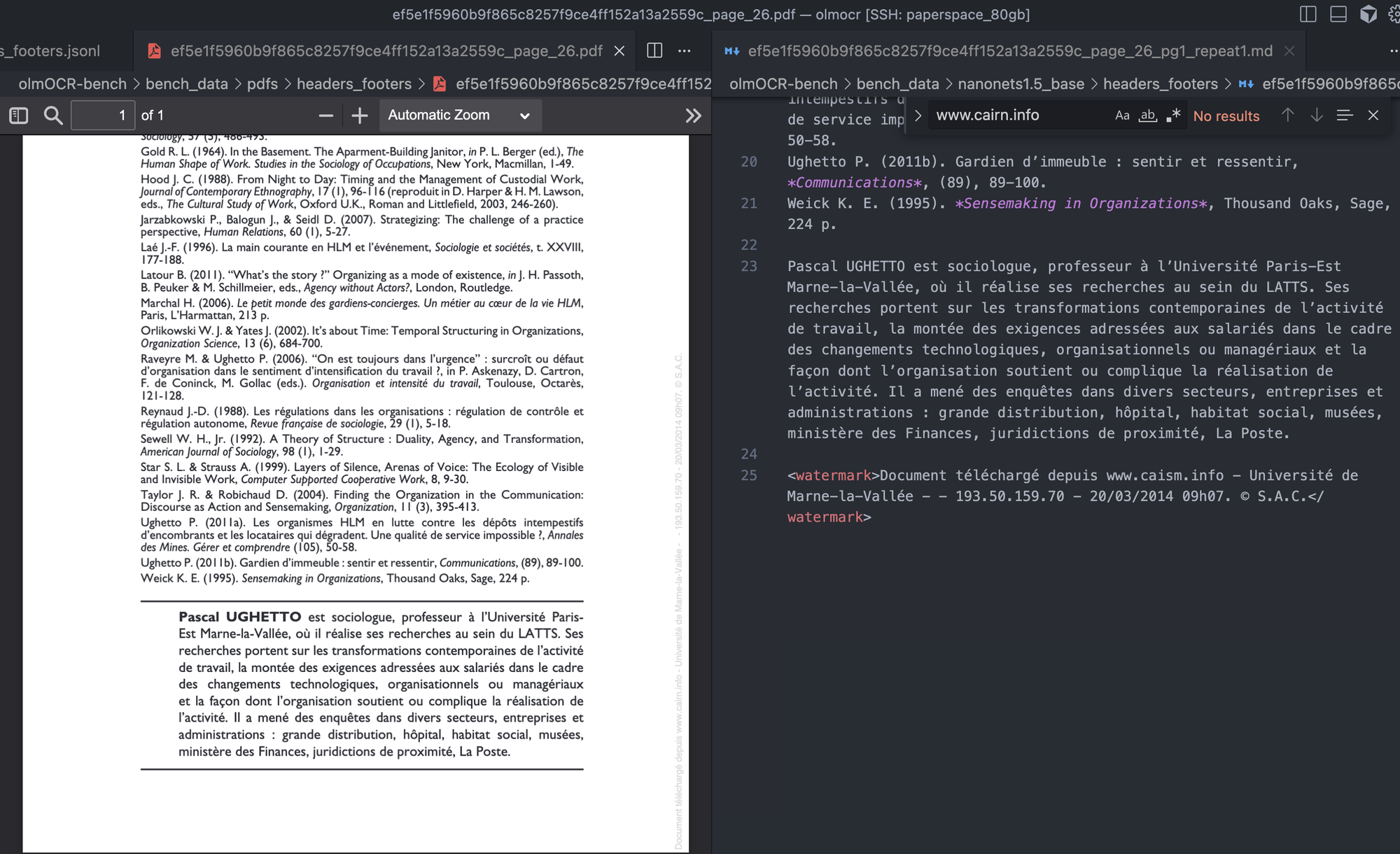
For the above picture, Nanonets-OCR2 accurately predicts the watermark to the fitting aspect of the picture, however within the floor reality annotation penalizes the mannequin for predicting it accurately.
{
"pdf": "headers_footers/ef5e1f5960b9f865c8257f9ce4ff152a13a2559c_page_26.pdf",
"web page": 1,
"id": "ef5e1f5960b9f865c8257f9ce4ff152a13a2559c_page_26.pdf_manual_01",
"kind": "absent",
"textual content": "Doc tu00e9lu00e9chargu00e9 depuis www.cairn.data - Universitu00e9 de Marne-la-Vallu00e9e - - 193.50.159.70 - 20/03/2014 09h07. u00a9 S.A.C.", "case_sensitive": false, "max_diffs": 3, "checked": "verified", "first_n": null, "last_n": null, "url": ""}
Kind absent implies that within the prediction knowledge, that textual content shouldn’t be current.
Instance 2
The benchmark additionally doesn’t take into account texts which are current within the doc footer.
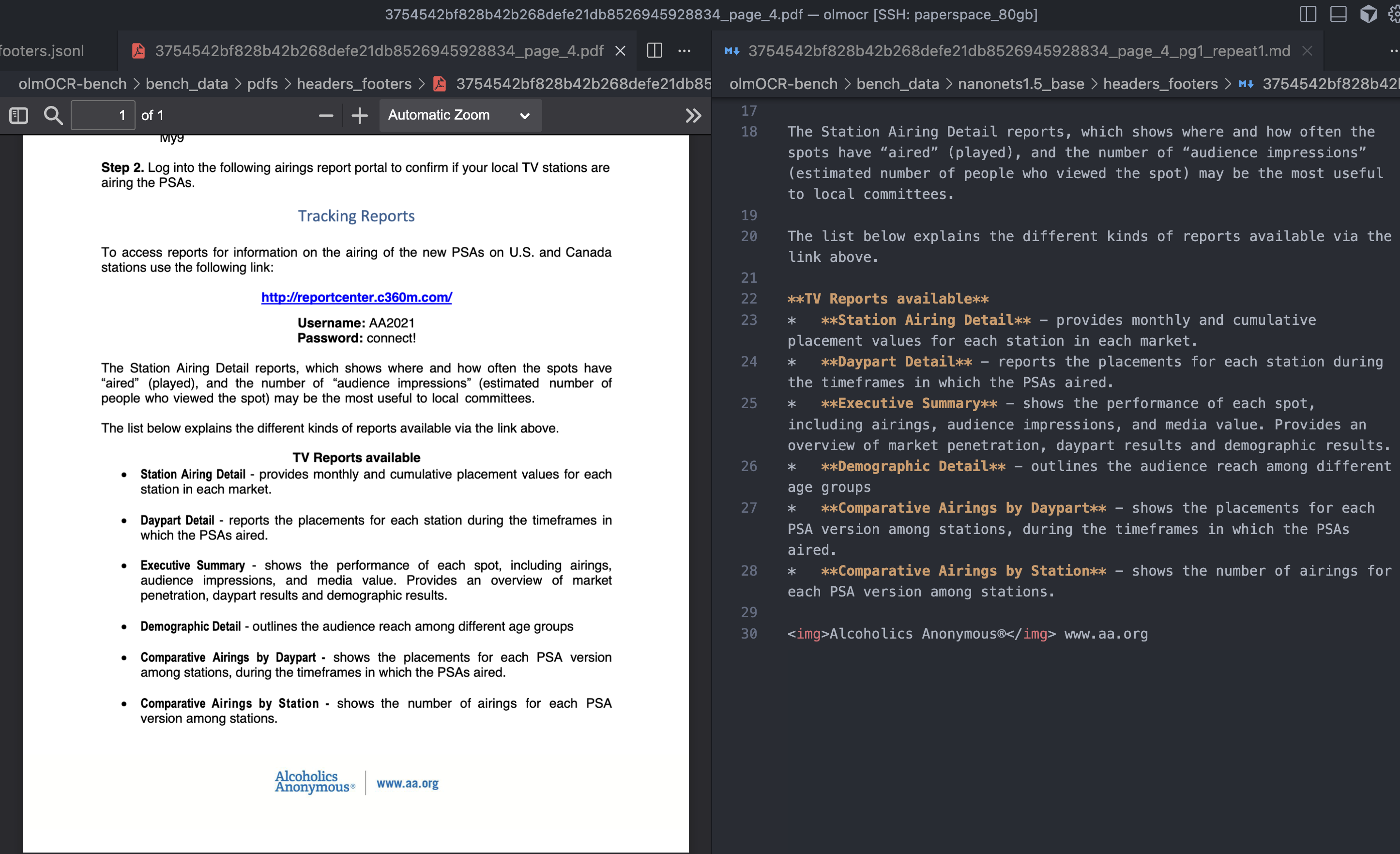
Instance on this doc, the Alcoholics Namelessu00ae and www.aa.org shouldn’t be current within the doc in line with the ground-truth, which is inaccurate
{
"pdf": "headers_footers/3754542bf828b42b268defe21db8526945928834_page_4.pdf",
"web page": 1,
"id": "3754542bf828b42b268defe21db8526945928834_page_4_header_00",
"kind": "absent",
"max_diffs": 0,
"checked": "verified",
"url": "",
"textual content": "Alcoholics Namelessu00ae",
"case_sensitive": false, "first_n": null, "last_n": null
}
{
"pdf": "headers_footers/3754542bf828b42b268defe21db8526945928834_page_4.pdf",
"web page": 1,
"id": "3754542bf828b42b268defe21db8526945928834_page_4_header_01",
"kind": "absent",
"max_diffs": 0,
"checked": "verified",
"url": "",
"textual content": "www.aa.org",
"case_sensitive": false, "first_n": null, "last_n": null}
Benchmark B: OmniDocBench
OmniDocBench reveals related points, however extra broadly:
- Equation analysis depends on strict LaTeX string equivalence.
- Semantically similar equations fail because of macro, spacing, or image variations.
- Quite a few ground-truth annotation errors have been noticed (lacking tokens, malformed math, incorrect spacing).
- Unicode normalization and spacing variations systematically cut back scores.
- Prediction choice heuristics can fail even when the proper reply is totally current.
In lots of circumstances, low scores mirror benchmark artifacts, not mannequin errors.
Instance 1

Within the instance above, the Nanonets-OCR2-3B predicts 5 g silica + 3 g Al$_2$O$_3$ however the floor reality expects as $ 5g \mathrm{\ s i l i c a}+3g \mathrm{\ A l}*{2} \mathrm{O*{3}} $ . This flags the mannequin prediction as incorrect, even when each are appropriate.
Full Floor Fact and Prediction, and the take a look at case shared under:
'pred': 'The collected eluant was concentrated by rotary evaporator to 1 ml. The extracts have been lastly handed via a remaining column crammed with 5 g silica + 3 g Al$_2$O$_3$ to take away any co-extractive compounds which will trigger instrumental interferences durin the evaluation. The extract was eluted with 120 ml of DCM:n-hexane (1:1), the primary 18 ml of eluent was discarded and the remainder have been collected, which accommodates the analytes of curiosity. The extract was exchanged into n-hexane, concentrated to 1 ml to which 1 μg/ml of inner commonplace was added.'
'gt': 'The collected eluant was concentrated by rotary evaporator to 1 ml .The extracts have been lastly handed via a remaining column crammed with $ 5g \mathrm{\ s i l i c a}+3g \mathrm{\ A l}*{2} \mathrm{O*{3}} $ to take away any co-extractive compounds which will trigger instrumental
interferences through the evaluation. The extract was eluted with 120 ml of DCM:n-hexane (1:1), the primary 18 ml of eluent was discarded and the remainder have been collected, which accommodates the analytes of curiosity. The extract was exchanged into n - hexane, concentrated to 1 ml to which $ \mu\mathrm{g / ml} $ of inner commonplace was added.'Instance 2
We discovered considerably extra incorrect annotations with OmniDocBench

Within the ground-truth annotation 1 is lacking in 1 ml .
'textual content': 'The collected eluant was concentrated by rotary evaporator to 1 ml .The extracts have been lastly handed via a remaining column crammed with $ 5g \mathrm{\ s i l i c a}+3g \mathrm{\ A l}*{2} \mathrm{O*{3}} $ to take away any co-extractive compounds which will trigger instrumental interferences through the evaluation. The extract was eluted with 120 ml of DCM:n-hexane (1:1), the primary 18 ml of eluent was discarded and the remainder have been collected, which accommodates the analytes of curiosity. The extract was exchanged into n - hexane, concentrated to 1 ml to which $ \mu\mathrm{g / ml} $ of inner commonplace was added.'

