Service templates are a typical constructing block within the “golden paths” organisations construct for his or her engineering groups, to make it simple to do the correct factor. The templates are alleged to be the position fashions for all of the companies within the organisation, all the time representing the hottest coding patterns and requirements.
One of many challenges with service templates although is that when a staff instantiated a service with one, it’s tedious to feed template updates again to these companies. Can GenAI assist with that?
Reference software as pattern supplier
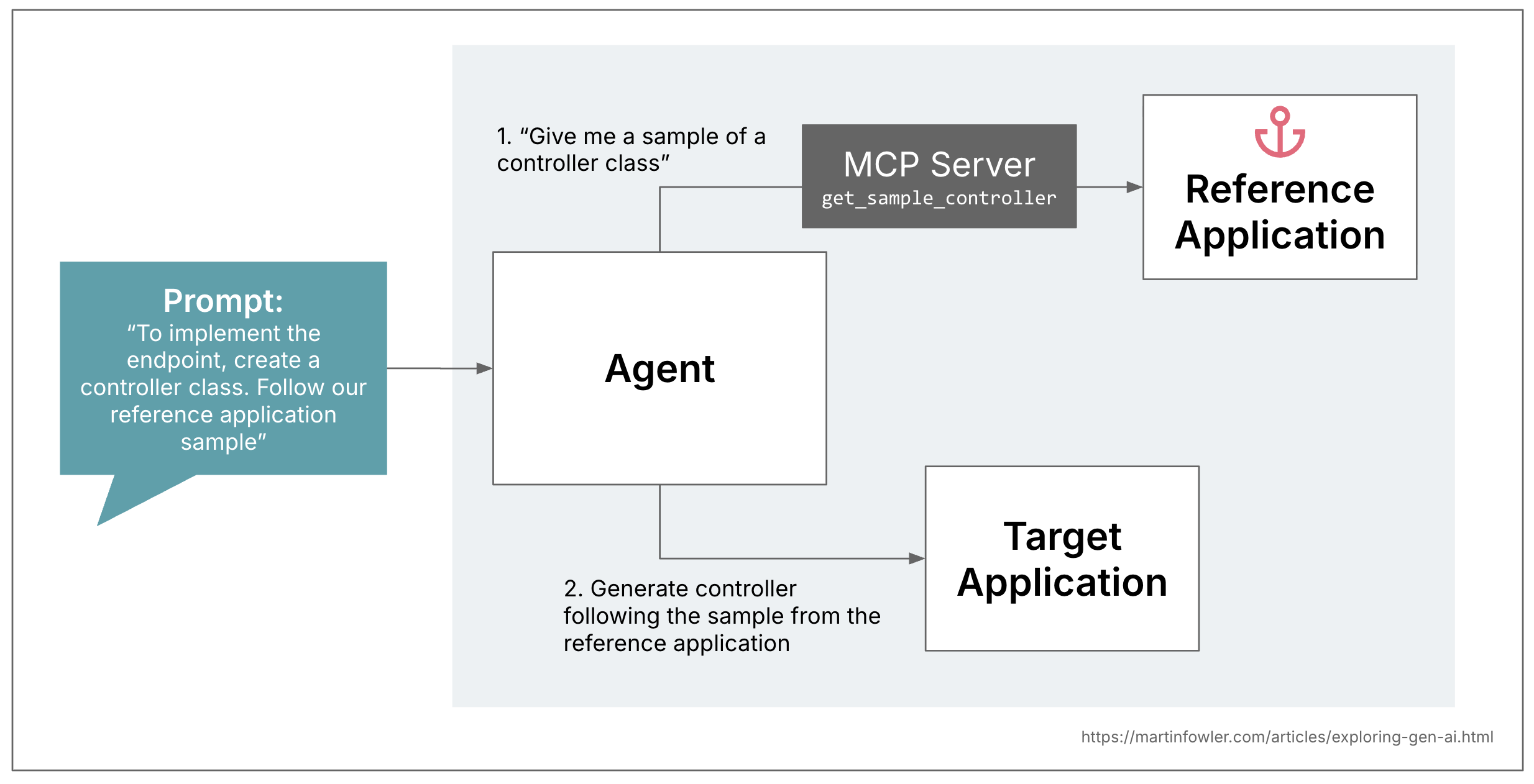
As half of a bigger experiment that I lately wrote about right here, I created an MCP server that offers a coding assistant entry to coding samples for typical patterns. In my case, this was for a Spring Boot internet software, the place the patterns had been repository, service and controller lessons. It’s a effectively established prompting apply at this level that offering LLMs with examples of the outputs that we would like results in higher outcomes. To place “offering examples” into fancier phrases: That is additionally known as “few-shot prompting”, or “in-context studying”.
Once I began working with code samples in prompts, I rapidly realised how tedious this was, as a result of I used to be working in a pure language markdown file. It felt just a little bit like writing my first Java exams at college, in pencil: You will have know concept if the code you’re writing truly compiles. And what’s extra, when you’re creating prompts for a number of coding patterns, you wish to maintain them per one another. Sustaining code samples in a reference software venture that you would be able to compile and run (like a service template) makes it loads simpler to supply AI with compilable, constant samples.
Detect drift from the reference software
Now again to the issue assertion I discussed firstly: As soon as code is generated (be that with AI, or with a service template), after which additional prolonged and maintained, codebases usually drift away from the position mannequin of the reference software.
So in a second step, I puzzled how we would use this strategy to do a “code sample drift detection” between the codebase and the reference software. I examined this with a comparatively easy instance, I added a logger and log.debug statements to the reference software’s controller lessons:
Then I expanded the MCP server to supply entry to the git commits within the reference software. Asking the agent to first search for the precise modifications within the reference offers me some management over the scope of the drift detection, I can use the commits to speak to AI precisely what kind of drift I’m thinking about. Earlier than I launched this, after I simply requested AI to match the reference controllers with the present controllers, it went a bit overboard with numerous irrelevant comparisons, and I noticed this commit-scoping strategy have an excellent affect.
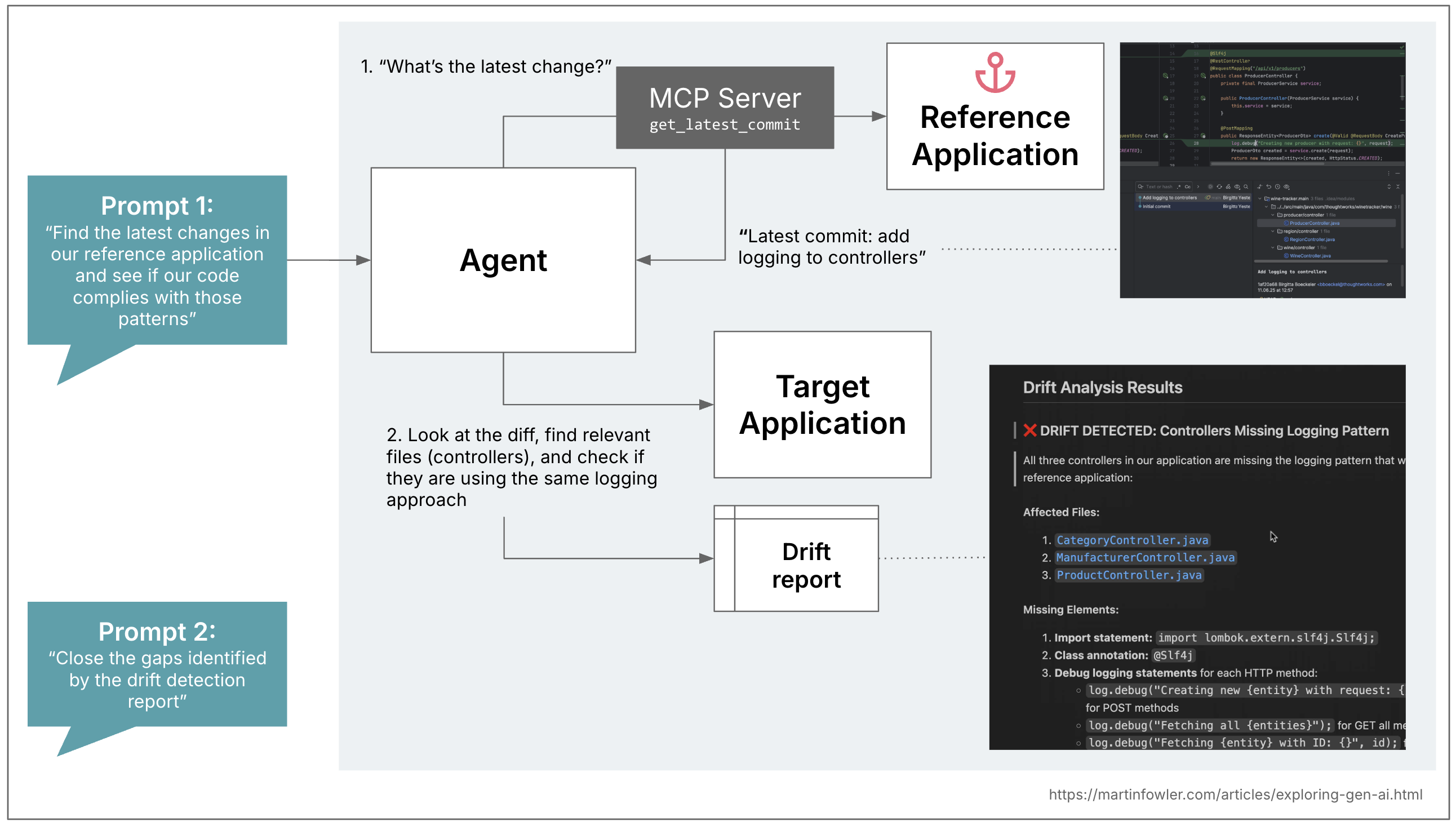
In step one, I simply requested AI to generate a report for me that recognized all of the drift, so I might overview and edit that report, e.g. take away findings that had been irrelevant. Within the second step, I requested AI to take the report and write code that closes the gaps recognized.
When is AI bringing one thing new to the desk?
A factor so simple as including a logger, or altering a logging framework, may also be performed deterministically by codemod instruments like OpenRewrite. So bear that in thoughts earlier than you attain for AI.
The place AI can shine is at any time when now we have drift that wants coding that’s extra dynamic than is feasible with regular-expression-based codemod recipes. In a sophisticated type of the logging instance, this may be turning non-standardised, wealthy log statements right into a structured format, the place an LLM may be higher at turning all kinds of present log messages into the respective construction.
The instance MCP server is included in the repository that accompanies the unique article.

