TL;DR:
CIOs face mounting strain to undertake agentic AI — however skipping steps results in value overruns, compliance gaps, and complexity you may’t unwind. This put up outlines a better, staged path that will help you scale AI with management, readability, and confidence.
AI leaders are underneath immense strain to implement options which might be each cost-effective and safe. The problem lies not solely in adopting AI but in addition in preserving tempo with developments that may really feel overwhelming.
This usually results in the temptation to dive headfirst into the most recent improvements to remain aggressive.
Nevertheless, leaping straight into complicated multi-agent methods with no strong basis is akin to developing the higher flooring of a constructing earlier than laying its base, leading to a construction that’s unstable and probably hazardous.
On this put up, we stroll by methods to information your group by every stage of agentic AI maturity — securely, effectively, and with out expensive missteps.
Understanding key AI ideas
Earlier than delving into the levels of AI maturity, it’s important to ascertain a transparent understanding of key ideas:
Deterministic methods
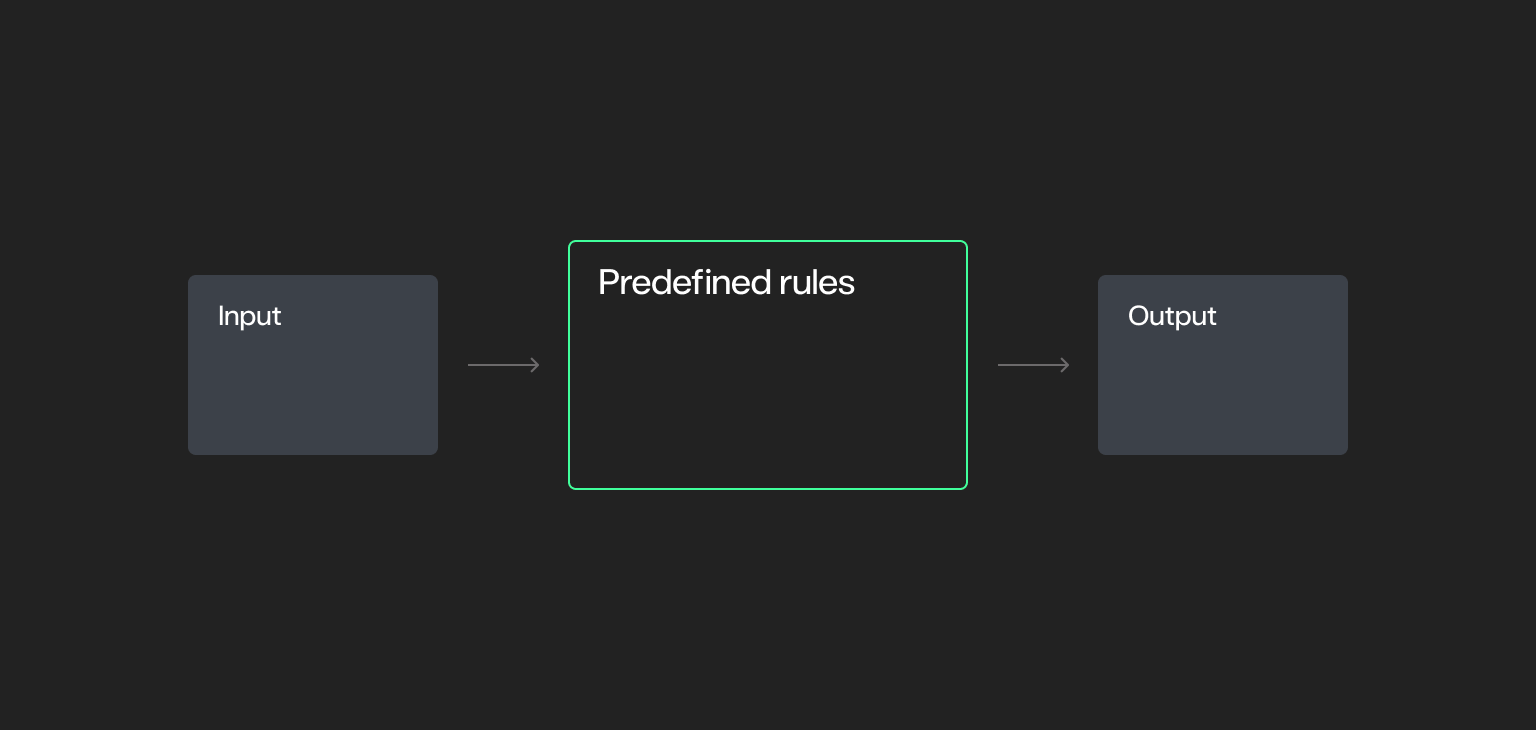
Deterministic methods are the foundational constructing blocks of automation.
- Observe a set set of predefined guidelines the place the end result is absolutely predictable. Given the identical enter, the system will all the time produce the identical output.
- Doesn’t incorporate randomness or ambiguity.
- Whereas all deterministic methods are rule-based, not all rule-based methods are deterministic.
- Preferrred for duties requiring consistency, traceability, and management.
- Examples: Primary automation scripts, legacy enterprise software program, and scheduled information switch processes.
Rule-based methods
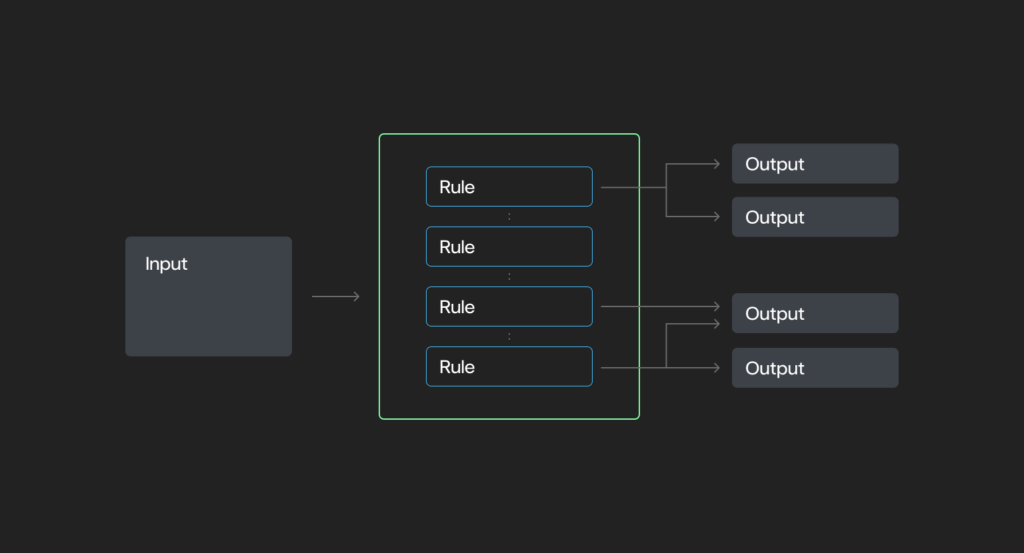
A broader class that features deterministic methods however may introduce variability (e.g., stochastic conduct).
- Function primarily based on a set of predefined situations and actions — “if X, then Y.”
- Could incorporate: deterministic methods or stochastic components, relying on design.
- Highly effective for implementing construction.
- Lack autonomy or reasoning capabilities.
- Examples: Electronic mail filters, Robotic Course of Automation (RPA) ) and complicated infrastructure protocols like web routing.
Course of AI
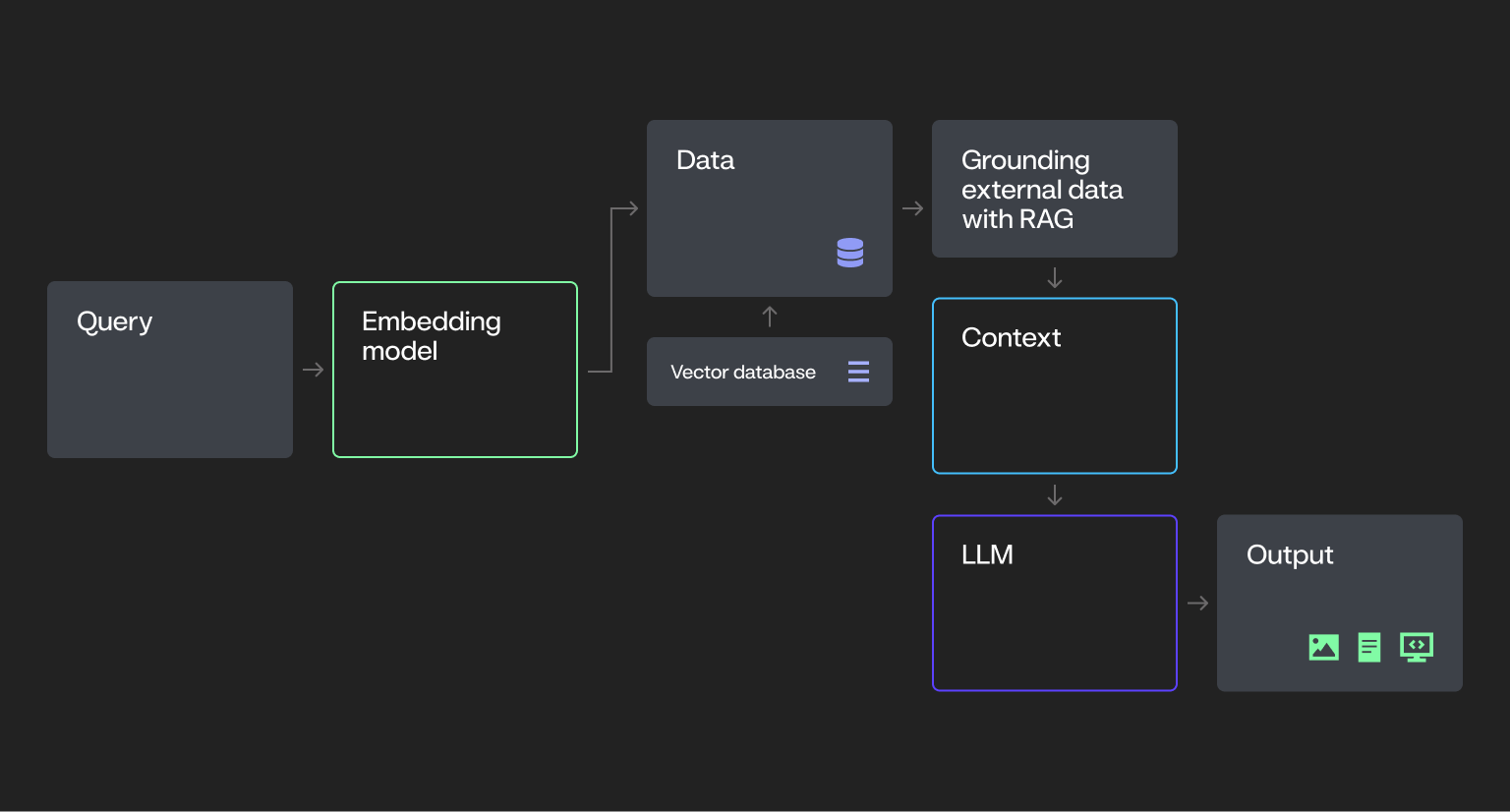
A step past rule-based methods.
- Powered by Giant Language Fashions (LLMs) and Imaginative and prescient-Language Fashions (VLMs)
- Skilled on intensive datasets to generate numerous content material (e.g., textual content, photographs, code) in response to enter prompts.
- Responses are grounded in pre-trained data and might be enriched with exterior information by way of methods like Retrieval-Augmented Technology (RAG).
- Doesn’t make autonomous selections — operates solely when prompted.
- Examples: Generative AI chatbots, summarization instruments, and content-generation functions powered by LLMs.
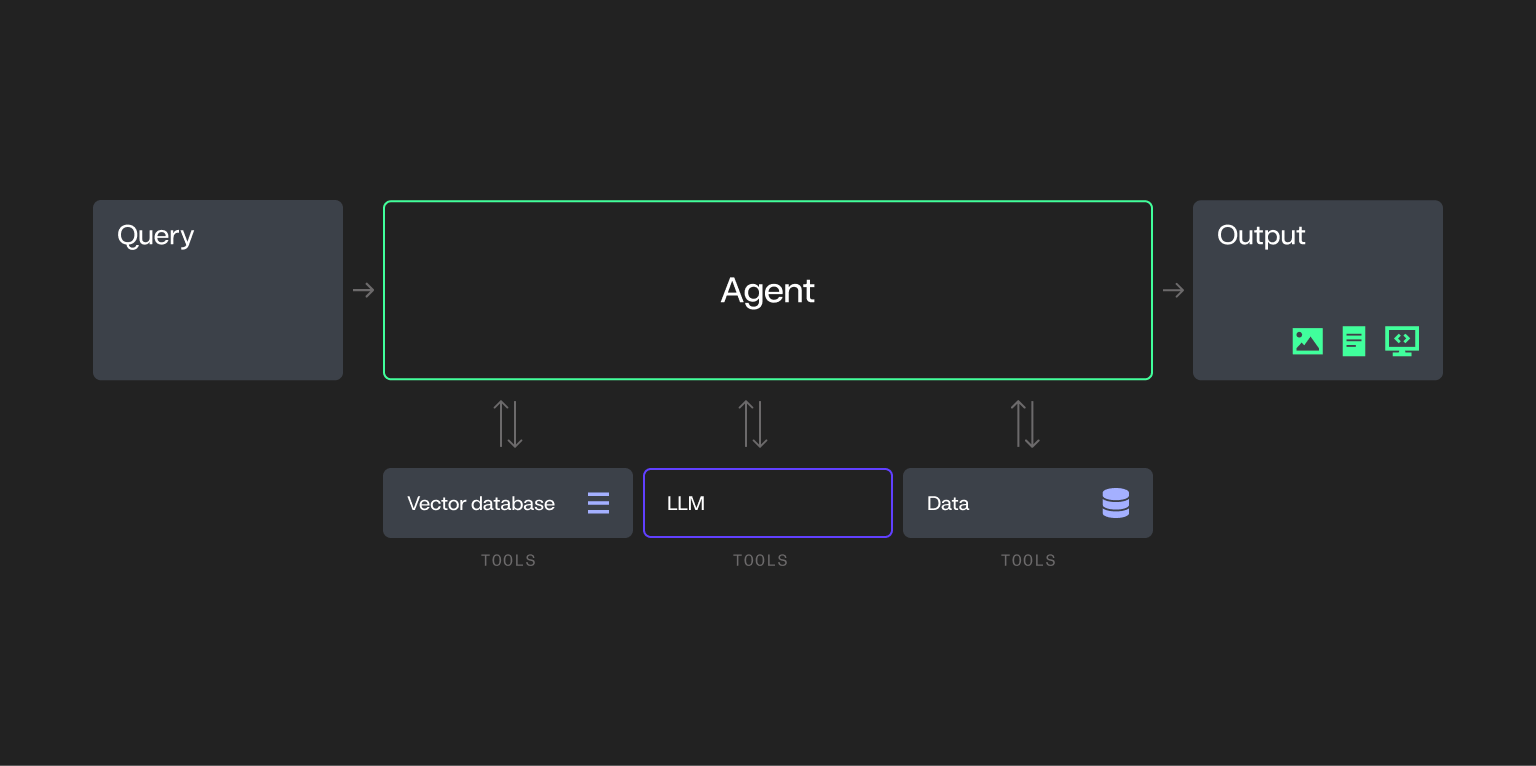
Single-agent methods
Introduce autonomy, planning, and power utilization, elevating foundational AI into extra complicated territory.
- AI-driven applications designed to carry out particular duties independently.
- Can combine with exterior instruments and methods (e.g., databases or APIs) to finish duties.
- Don’t collaborate with different brokers — function alone inside a process framework.
- To not be confused with RPA: RPA is good for extremely standardized, rules-based duties the place logic doesn’t require reasoning or adaptation.
- Examples: AI-driven assistants for forecasting, monitoring, or automated process execution that function independently.
Multi-agent methods
Essentially the most superior stage, that includes distributed decision-making, autonomous coordination, and dynamic workflows.
- Comprised of a number of AI brokers that work together and collaborate to realize complicated targets.
- Brokers dynamically resolve which instruments to make use of, when, and in what sequence.
- Capabilities embody planning, reflection, reminiscence utilization, and cross-agent collaboration.
- Examples: Distributed AI methods coordinating throughout departments like provide chain, customer support, or fraud detection.
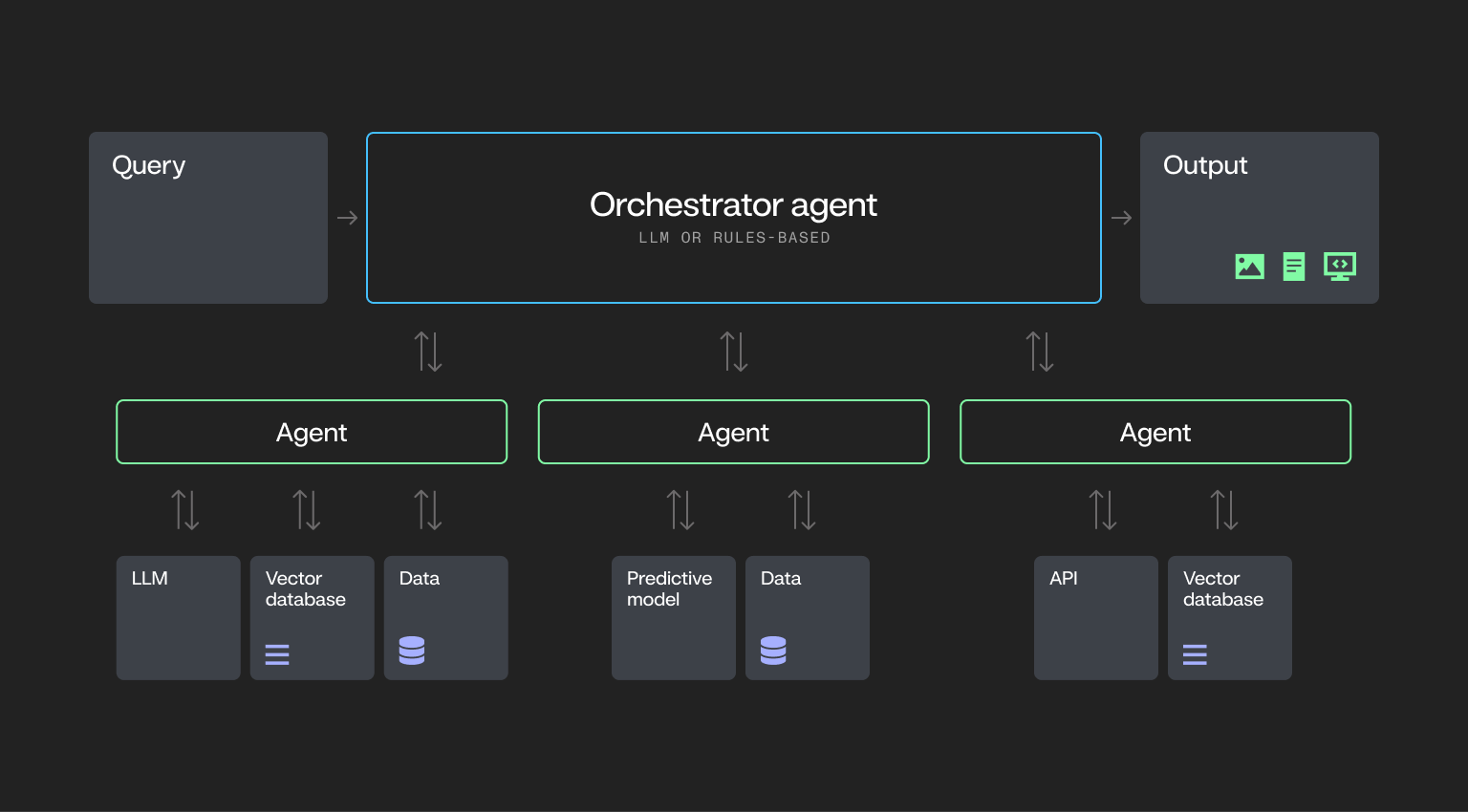
What makes an AI system actually agentic?
To be thought-about actually agentic, an AI system usually demonstrates core capabilities that allow it to function with autonomy and flexibility:
- Planning. The system can break down a process into steps and create a plan of execution.
- Software calling. The AI selects and makes use of instruments (e.g., fashions, capabilities) and initiates API calls to work together with exterior methods to finish duties.
- Adaptability. The system can regulate its actions in response to altering inputs or environments, making certain efficient efficiency throughout various contexts.
- Reminiscence. The system retains related data throughout steps or classes.
These traits align with broadly accepted definitions of agentic AI, together with frameworks mentioned by AI leaders similar to Andrew Ng.
Video: course of AI vs single-agent methods
With these definitions in thoughts, right here’s a fast video explaining the distinction between course of AI and single-agent methods.
Understanding agentic AI maturity levels
For the needs of simplicity, we’ve delineated the trail to extra complicated agentic flows into three levels. Every stage presents distinctive challenges and alternatives regarding value, safety, and governance.
Stage 1: Course of AI
What this stage appears like
Within the Course of AI stage, organizations usually pilot generative AI by remoted use instances like chatbots, doc summarization, or inner Q&A. These efforts are sometimes led by innovation groups or particular person enterprise models, with restricted involvement from IT.
Deployments are constructed round a single LLM and function exterior core methods like ERP or CRM, making integration and oversight troublesome.
Infrastructure is usually pieced collectively, governance is casual, and safety measures could also be inconsistent.
Provide chain instance for course of AI
Within the Course of AI stage, a provide chain workforce may use a generative AI-powered chatbot to summarize cargo information or reply primary vendor queries primarily based on inner paperwork. This software can pull in information by a RAG workflow to offer insights, but it surely doesn’t take any motion autonomously.
For instance, the chatbot may summarize stock ranges, predict demand primarily based on historic tendencies, and generate a report for the workforce to assessment. Nevertheless, the workforce should then resolve what motion to take (e.g., place restock orders or regulate provide ranges).
The system merely gives insights — it doesn’t make selections or take actions.
Frequent obstacles
Whereas early AI initiatives can present promise, they usually create operational blind spots that stall progress, drive up prices, and enhance threat if left unaddressed.
- Knowledge integration and high quality. Most organizations battle to unify information throughout disconnected methods, limiting the reliability and relevance of generative AI output.
- Scalability challenges. Pilot initiatives usually stall when groups lack the infrastructure, entry, or technique to maneuver from proof of idea to manufacturing.
- Insufficient testing and stakeholder alignment. Generative outputs are continuously launched with out rigorous QA or enterprise person acceptance, resulting in belief and adoption points.
- Change administration friction. As generative AI reshapes roles and workflows, poor communication and planning can create organizational resistance.
- Lack of visibility and traceability. With out mannequin monitoring or auditability, it’s obscure how selections are made or pinpoint the place errors happen.
- Bias and equity dangers. Generative fashions can reinforce or amplify bias in coaching information, creating reputational, moral, or compliance dangers.
- Moral and accountability gaps. AI-generated content material can blur moral traces or be misused, elevating questions round accountability and management.
- Regulatory complexity. Evolving world and industry-specific rules make it troublesome to make sure ongoing compliance at scale.
Software and infrastructure necessities
Earlier than advancing to extra autonomous methods, organizations should guarantee their infrastructure is supplied to help safe, scalable, and cost-effective AI deployment.
- Quick, versatile vector database updates to handle embeddings as new information turns into obtainable.
- Scalable information storage to help giant datasets used for coaching, enrichment, and experimentation.
- Adequate compute sources (CPUs/GPUs) to energy coaching, tuning, and operating fashions at scale.
- Safety frameworks with enterprise-grade entry controls, encryption, and monitoring to guard delicate information.
- Multi-model flexibility to check and consider totally different LLMs and decide one of the best match for particular use instances.
- Benchmarking instruments to visualise and examine mannequin efficiency throughout assessments and testing.
- Lifelike, domain-specific information to check responses, simulate edge instances, and validate outputs.
- A QA prototyping atmosphere that helps fast setup, person acceptance testing, and iterative suggestions.
- Embedded safety, AI, and enterprise logic for consistency, guardrails, and alignment with organizational requirements.
- Actual-time intervention and moderation instruments for IT and safety groups to watch and management AI outputs in actual time.
- Strong information integration capabilities to attach sources throughout the group and guarantee high-quality inputs.
- Elastic infrastructure to scale with demand with out compromising efficiency or availability.
- Compliance and audit tooling that permits documentation, change monitoring, and regulatory adherence.
Making ready for the following stage
To construct on early generative AI efforts and put together for extra autonomous methods, organizations should lay a strong operational and organizational basis.
- Spend money on AI-ready information. It doesn’t should be good, but it surely have to be accessible, structured, and safe to help future workflows.
- Use vector database visualizations. This helps groups establish data gaps and validate the relevance of generative responses.
- Apply business-driven QA/UAT. Prioritize acceptance testing with the top customers who will depend on generative output, not simply technical groups.
- Arise a safe AI registry. Observe mannequin variations, prompts, outputs, and utilization throughout the group to allow traceability and auditing.
- Implement baseline governance. Set up foundational frameworks like role-based entry management (RBAC), approval flows, and information lineage monitoring.
- Create repeatable workflows. Standardize the AI growth course of to maneuver past one-off experimentation and allow scalable output.
- Construct traceability into generative AI utilization. Guarantee transparency round information sources, immediate building, output high quality, and person exercise.
- Mitigate bias early. Use numerous, consultant datasets and commonly audit mannequin outputs to establish and handle equity dangers.
- Collect structured suggestions. Set up suggestions loops with finish customers to catch high quality points, information enhancements, and refine use instances.
- Encourage cross-functional oversight. Contain authorized, compliance, information science, and enterprise stakeholders to information technique and guarantee alignment.
Key takeaways
Course of AI is the place most organizations start — but it surely’s additionally the place many get caught. With out sturdy information foundations, clear governance, and scalable workflows, early experiments can introduce extra threat than worth.
To maneuver ahead, CIOs must shift from exploratory use instances to enterprise-ready methods — with the infrastructure, oversight, and cross-functional alignment required to help protected, safe, and cost-effective AI adoption at scale.
Stage 2: Single-agent methods
What this stage appears like
At this stage, organizations start tapping into true agentic AI — deploying single-agent methods that may act independently to finish duties. These brokers are able to planning, reasoning, and calling instruments like APIs or databases to get work performed with out human involvement.
Not like earlier generative methods that anticipate prompts, single-agent methods can resolve when and methods to act inside an outlined scope.
This marks a transparent step into autonomous operations—and a important inflection level in a corporation’s AI maturity.
Provide chain instance for single-agent methods
Let’s revisit the provide chain instance. With a single-agent system in place, the workforce can now autonomously handle stock. The system screens real-time inventory ranges throughout regional warehouses, forecasts demand utilizing historic tendencies, and locations restock orders robotically by way of an built-in procurement API—with out human enter.
Not like the method AI stage, the place a chatbot solely summarizes information or solutions queries primarily based on prompts, the single-agent system acts autonomously. It makes selections, adjusts stock, and locations orders inside a predefined workflow.
Nevertheless, as a result of the agent is making unbiased selections, any errors in configuration or missed edge instances (e.g., sudden demand spikes) may lead to points like stockouts, overordering, or pointless prices.
This can be a important shift. It’s not nearly offering data anymore; it’s in regards to the system making selections and executing actions, making governance, monitoring, and guardrails extra essential than ever.
Frequent obstacles
As single-agent methods unlock extra superior automation, many organizations run into sensible roadblocks that make scaling troublesome.
- Legacy integration challenges. Many single-agent methods battle to attach with outdated architectures and information codecs, making integration technically complicated and resource-intensive.
- Latency and efficiency points. As brokers carry out extra complicated duties, delays in processing or software calls can degrade person expertise and system reliability.
- Evolving compliance necessities. Rising rules and moral requirements introduce uncertainty. With out strong governance frameworks, staying compliant turns into a shifting goal.
- Compute and expertise calls for. Operating agentic methods requires vital infrastructure and specialised abilities, placing strain on budgets and headcount planning.
- Software fragmentation and vendor lock-in. The nascent agentic AI panorama makes it exhausting to decide on the precise tooling. Committing to a single vendor too early can restrict flexibility and drive up long-term prices.
- Traceability and power name visibility. Many organizations lack the required stage of observability and granular intervention required for these methods. With out detailed traceability and the power to intervene at a granular stage, methods can simply run amok, resulting in unpredictable outcomes and elevated threat.
Software and infrastructure necessities
At this stage, your infrastructure must do extra than simply help experimentation—it must maintain brokers related, operating easily, and working securely at scale.
- Integration platform with instruments that facilitate seamless connectivity between the AI agent and your core enterprise methods, making certain clean information circulate throughout environments.
- Monitoring methods designed to trace and analyze the agent’s efficiency and outcomes, flag points, and floor insights for ongoing enchancment.
- Compliance administration instruments that assist implement AI insurance policies and adapt rapidly to evolving regulatory necessities.
- Scalable, dependable storage to deal with the rising quantity of knowledge generated and exchanged by AI brokers.
- Constant compute entry to maintain brokers performing effectively underneath fluctuating workloads.
- Layered safety controls that defend information, handle entry, and keep belief as brokers function throughout methods.
- Dynamic intervention and moderation that may perceive processes aren’t adhering to insurance policies, intervene in real-time and ship alerts for human intervention.
Making ready for the following stage
Earlier than layering on further brokers, organizations must take inventory of what’s working, the place the gaps are, and methods to strengthen coordination, visibility, and management at scale.
- Consider present brokers. Establish efficiency limitations, system dependencies, and alternatives to enhance or increase automation.
- Construct coordination frameworks. Set up methods that may help seamless interplay and task-sharing between future brokers.
- Strengthen observability. Implement monitoring instruments that present real-time insights into agent conduct, outputs, and failures on the software stage and the agent stage.
- Have interaction cross-functional groups. Align AI targets and threat administration methods throughout IT, authorized, compliance, and enterprise models.
- Embed automated coverage enforcement. Construct in mechanisms that uphold safety requirements and help regulatory compliance as agent methods increase.
Key takeaways
Single-agent methods provide vital functionality by enabling autonomous actions that improve operational effectivity. Nevertheless, they usually include increased prices in comparison with non-agentic RAG workflows, like these within the course of AI stage, in addition to elevated latency and variability in response instances.
Since these brokers make selections and take actions on their very own, they require tight integration, cautious governance, and full traceability.
If foundational controls like observability, governance, safety, and auditability aren’t firmly established within the course of AI stage, these gaps will solely widen, exposing the group to higher dangers round value, compliance, and model popularity.
Stage 3: Multi-agent methods
What this stage appears like
On this stage, a number of AI brokers work collectively — every with its personal process, instruments, and logic — to realize shared targets with minimal human involvement. These brokers function autonomously, however additionally they coordinate, share data, and regulate their actions primarily based on what others are doing.
Not like single-agent methods, selections aren’t made in isolation. Every agent acts primarily based by itself observations and context, contributing to a system that behaves extra like a workforce, planning, delegating, and adapting in actual time.
This type of distributed intelligence unlocks highly effective use instances and big scale. However as one can think about, it additionally introduces vital operational complexity: overlapping selections, system interdependencies, and the potential for cascading failures if brokers fall out of sync.
Getting this proper calls for sturdy structure, real-time observability, and tight controls.
Provide chain instance for multi-agent methods
In earlier levels, a chatbot was used to summarize shipments and a single-agent system was deployed to automate stock restocking.
On this provide chain instance, a community of AI brokers are deployed, every specializing in a unique a part of the operation, from forecasting and video evaluation to scheduling and logistics.
When an sudden cargo quantity is forecasted, brokers kick into motion:
- A forecasting agent initiatives capability wants.
- A pc imaginative and prescient agent analyzes reside warehouse footage to search out underutilized area.
- A delay prediction agent faucets time sequence information to anticipate late arrivals.
These brokers talk and coordinate in actual time, adjusting workflows, updating the warehouse supervisor, and even triggering downstream modifications like rescheduling vendor pickups.
This stage of autonomy unlocks pace and scale that guide processes can’t match. However it additionally means one defective agent — or a breakdown in communication — can ripple throughout the system.
At this stage, visibility, traceability, intervention, and guardrails change into non-negotiable.
Frequent obstacles
The shift to multi-agent methods isn’t only a step up in functionality — it’s a leap in complexity. Every new agent added to the system introduces new variables, new interdependencies, and new methods for issues to interrupt in case your foundations aren’t strong.
- Escalating infrastructure and operational prices. Operating multi-agent methods is pricey—particularly as every agent drives further API calls, orchestration layers, and real-time compute calls for. Prices compound rapidly throughout a number of fronts:
- Specialised tooling and licenses. Constructing and managing agentic workflows usually requires area of interest instruments or frameworks, rising prices and limiting flexibility.
- Useful resource-intensive compute. Multi-agent methods demand high-performance {hardware}, like GPUs, which might be expensive to scale and troublesome to handle effectively.
- Scaling the workforce. Multi-agent methods require area of interest experience throughout AI, MLOps, and infrastructure — usually including headcount and rising payroll prices in an already aggressive expertise market.
- Operational overhead. Even autonomous methods want hands-on help. Standing up and sustaining multi-agent workflows usually requires vital guide effort from IT and infrastructure groups, particularly throughout deployment, integration, and ongoing monitoring.
- Deployment sprawl. Managing brokers throughout cloud, edge, desktop, and cellular environments introduces considerably extra complexity than predictive AI, which generally depends on a single endpoint. Compared, multi-agent methods usually require 5x the coordination, infrastructure, and help to deploy and keep.
- Misaligned brokers. With out sturdy coordination, brokers can take conflicting actions, duplicate work, or pursue targets out of sync with enterprise priorities.
- Safety floor growth. Every further agent introduces a brand new potential vulnerability, making it more durable to guard methods and information end-to-end.
- Vendor and tooling lock-in. Rising ecosystems can result in heavy dependence on a single supplier, making future modifications expensive and disruptive.
- Cloud constraints. When multi-agent workloads are tied to a single supplier, organizations threat operating into compute throttling, burst limits, or regional capability points—particularly as demand turns into much less predictable and more durable to regulate.
- Autonomy with out oversight. Brokers might exploit loopholes or behave unpredictably if not tightly ruled, creating dangers which might be exhausting to comprise in actual time.
- Dynamic useful resource allocation. Multi-agent workflows usually require infrastructure that may reallocate compute (e.g., GPUs, CPUs) in actual time—including new layers of complexity and price to useful resource administration.
- Mannequin orchestration complexity. Coordinating brokers that depend on numerous fashions or reasoning methods introduces integration overhead and will increase the chance of failure throughout workflows.
- Fragmented observability. Tracing selections, debugging failures, or figuring out bottlenecks turns into exponentially more durable as agent rely and autonomy develop.
- No clear “performed.” With out sturdy process verification and output validation, brokers can drift off-course, fail silently, or burn pointless compute.
Software and infrastructure necessities
As soon as brokers begin making selections and coordinating with one another, your methods must do extra than simply sustain — they should keep in management. These are the core capabilities to have in place earlier than scaling multi-agent workflows in manufacturing.
- Elastic compute sources. Scalable entry to GPUs, CPUs, and high-performance infrastructure that may be dynamically reallocated to help intensive agentic workloads in actual time.
- Multi-LLM entry and routing. Flexibility to check, examine, and route duties throughout totally different LLMs to regulate prices and optimize efficiency by use case.
- Autonomous system safeguards. Constructed-in safety frameworks that stop misuse, defend information integrity, and implement compliance throughout distributed agent actions.
- Agent orchestration layer. Workflow orchestration instruments that coordinate process delegation, software utilization, and communication between brokers at scale.
- Interoperable platform structure. Open methods that help integration with numerous instruments and applied sciences, serving to you keep away from lock-in and enabling long-term flexibility.
- Finish-to-end dynamic observability and intervention. Monitoring, moderation, and traceability instruments that not solely floor agent conduct, detect anomalies, and help real-time intervention, but in addition adapt as brokers evolve. These instruments can establish when brokers try to take advantage of loopholes or create new ones, triggering alerts or halting processes to re-engage human oversight
Making ready for the following stage
There’s no playbook for what comes after multi-agent methods, however organizations that put together now would be the ones shaping what comes subsequent. Constructing a versatile, resilient basis is one of the simplest ways to remain forward of fast-moving capabilities, shifting rules, and evolving dangers.
- Allow dynamic useful resource allocation. Infrastructure ought to help real-time reallocation of GPUs, CPUs, and compute capability as agent workflows evolve.
- Implement granular observability. Use superior monitoring and alerting instruments to detect anomalies and hint agent conduct on the most detailed stage.
- Prioritize interoperability and adaptability. Select instruments and platforms that combine simply with different methods and help hot-swapping elements and streamlined CI/CD workflows so that you’re not locked into one vendor or tech stack.
- Construct multi-cloud fluency. Guarantee your groups can work throughout cloud platforms to distribute workloads effectively, scale back bottlenecks, keep away from provider-specific limitations, and help long-term flexibility.
- Centralize AI asset administration. Use a unified registry to control entry, deployment, and versioning of all AI instruments and brokers.
- Evolve safety together with your brokers. Implement adaptive, context-aware safety protocols that reply to rising threats in actual time.
- Prioritize traceability. Guarantee all agent selections are logged, explainable, and auditable to help investigation and steady enchancment.
- Keep present with instruments and techniques. Construct methods and workflows that may constantly check and combine new fashions, prompts, and information sources.
Key takeaways
Multi-agent methods promise scale, however with out the precise basis, they’ll amplify your issues, not remedy them.
As brokers multiply and selections change into extra distributed, even small gaps in governance, integration, or safety can cascade into expensive failures.
AI leaders who succeed at this stage gained’t be those chasing the flashiest demos—they’ll be those who deliberate for complexity earlier than it arrived.
Advancing to agentic AI with out dropping management
AI maturity doesn’t occur suddenly. Every stage — from early experiments to multi-agent methods— brings new worth, but in addition new complexity. The important thing isn’t to hurry ahead. It’s to maneuver with intention, constructing on sturdy foundations at each step.
For AI leaders, this implies scaling AI in methods which might be cost-effective, well-governed, and resilient to alter.
You don’t must do every little thing proper now, however the selections you make now form how far you’ll go.
Need to evolve by your AI maturity safely and effectively? Request a demo to see how our Agentic AI Apps Platform ensures safe, cost-effective development at every stage.

