
A menace actor is focusing on uncovered MongoDB cases in automated information extortion assaults demanding low ransoms from homeowners to revive the info.
The attacker focuses on the low-hanging fruit, databases which are insecure as a result of misconfiguration that allows entry with out restriction. Round 1,400 uncovered servers have been compromised, and the ransom word demanded a ransom of about $500 in Bitcoin.
Till 2021, a flurry of assaults had occurred, deleting 1000’s of databases and demanding ransom to revive the knowledge [1, 2]. Generally, the attacker simply deletes the databases with no monetary demand.
A pentesting train from researchers at cybersecurity firm Flare revealed that these assaults continued, solely at a smaller scale.
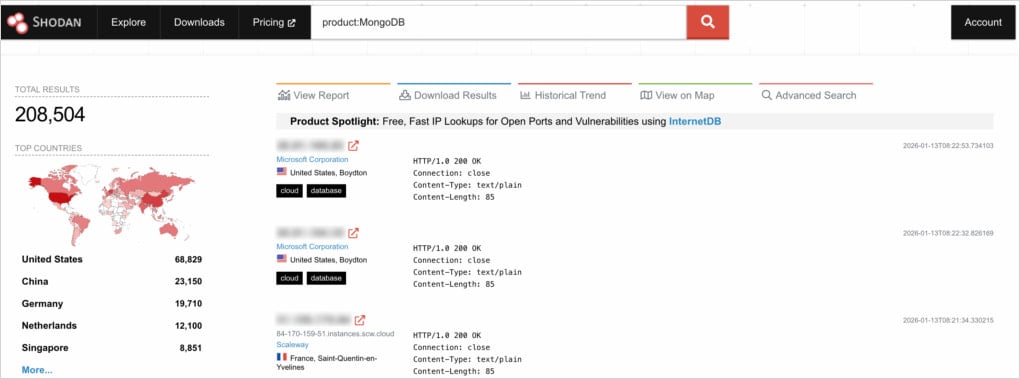
The researchers found greater than 208,500 publicly uncovered MongoDB servers. Of them, 100,000 expose operational data, and three,100 may very well be accessed with out authentication.
Supply: Flare
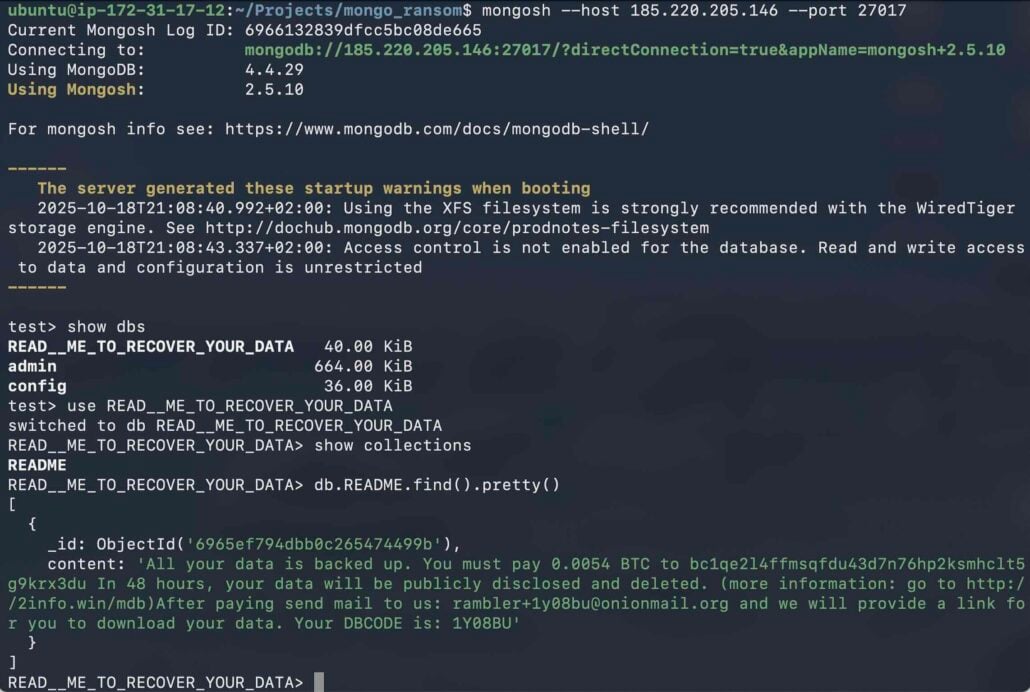
Nearly half (45.6%) of these with unrestricted entry had already been compromised when Flare examined them. The database had been wiped, and a ransom word was left.
An evaluation of the ransom notes confirmed that the majority of them demanded a fee of 0.005 BTC inside 48 hours.
“Risk actors demand fee in Bitcoin (usually round 0.005 BTC, equal right now to $500-600 USD) to a specified pockets tackle, promising to revive the info,” reads the Flare report.
“Nonetheless, there isn’t a assure the attackers have the info, or will present a working decryption key if paid.”
Supply: Flare
There have been solely 5 distinct pockets addresses throughout the dropped ransom notes, and considered one of them was prevalent in about 98% of the instances, indicating a single menace actor specializing in these assaults.
Flare additionally feedback on the remaining uncovered cases that didn’t seem to have been hit, though they have been uncovered and poorly secured, hypothesizing that these could have already paid a ransom to the attackers.
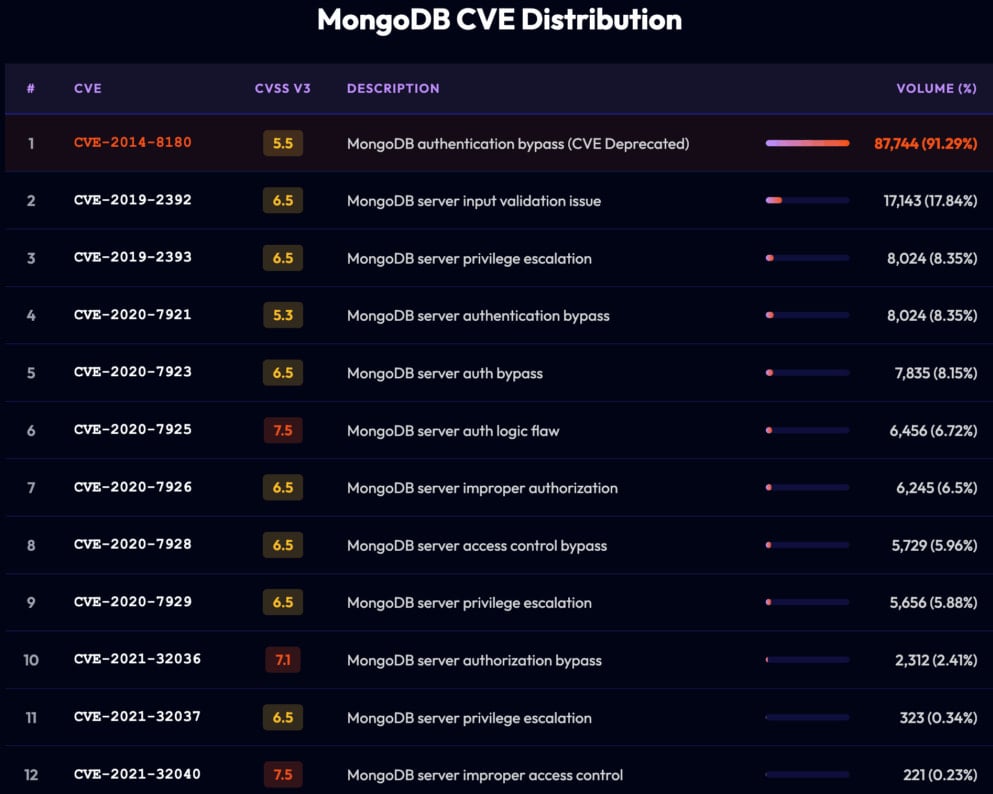
Along with poor authentication measures, the researchers additionally discovered that almost half (95,000) of all internet-exposed MongoDB servers run older variations which are weak to n-day flaws. Nonetheless, the potential of most of these was restricted to denial-of-service assaults, not providing distant code execution.
Supply: Flare
Flare means that MongoDB directors keep away from exposing cases to the general public until it’s completely essential, use sturdy authentication, implement firewall guidelines and Kubernetes community insurance policies that permit solely trusted connections, and keep away from copying configurations from deployment guides.
MongoDB needs to be up to date to the newest model and constantly monitored for publicity. Within the case of publicity, credentials must be rotated and logs examined for unauthorized exercise.



