
2025 noticed an enormous quantity of attacker innovation in relation to phishing assaults, as attackers proceed to double down on identity-based methods. The continuous evolution of phishing means it stays one of the vital efficient strategies accessible to attackers right this moment — in truth, it’s arguably simpler than ever.
Let’s take a better have a look at the important thing traits that outlined phishing assaults in 2025, and what these modifications imply for safety groups heading into 2026.
#1: Phishing goes omni-channel
We’ve been speaking concerning the rise of non-email phishing for a while now, however 2025 was the 12 months phishing really went omni-channel.
Though a lot of the business’s information on phishing nonetheless comes from e-mail safety distributors and instruments, the image is beginning to change. Roughly 1 in 3 phishing assaults detected by Push Safety had been delivered outdoors of e-mail.
There are lots of examples of phishing campaigns operated outdoors of e-mail, with LinkedIn DMs and Google Search being the highest channels we recognized. Notable campaigns embody:

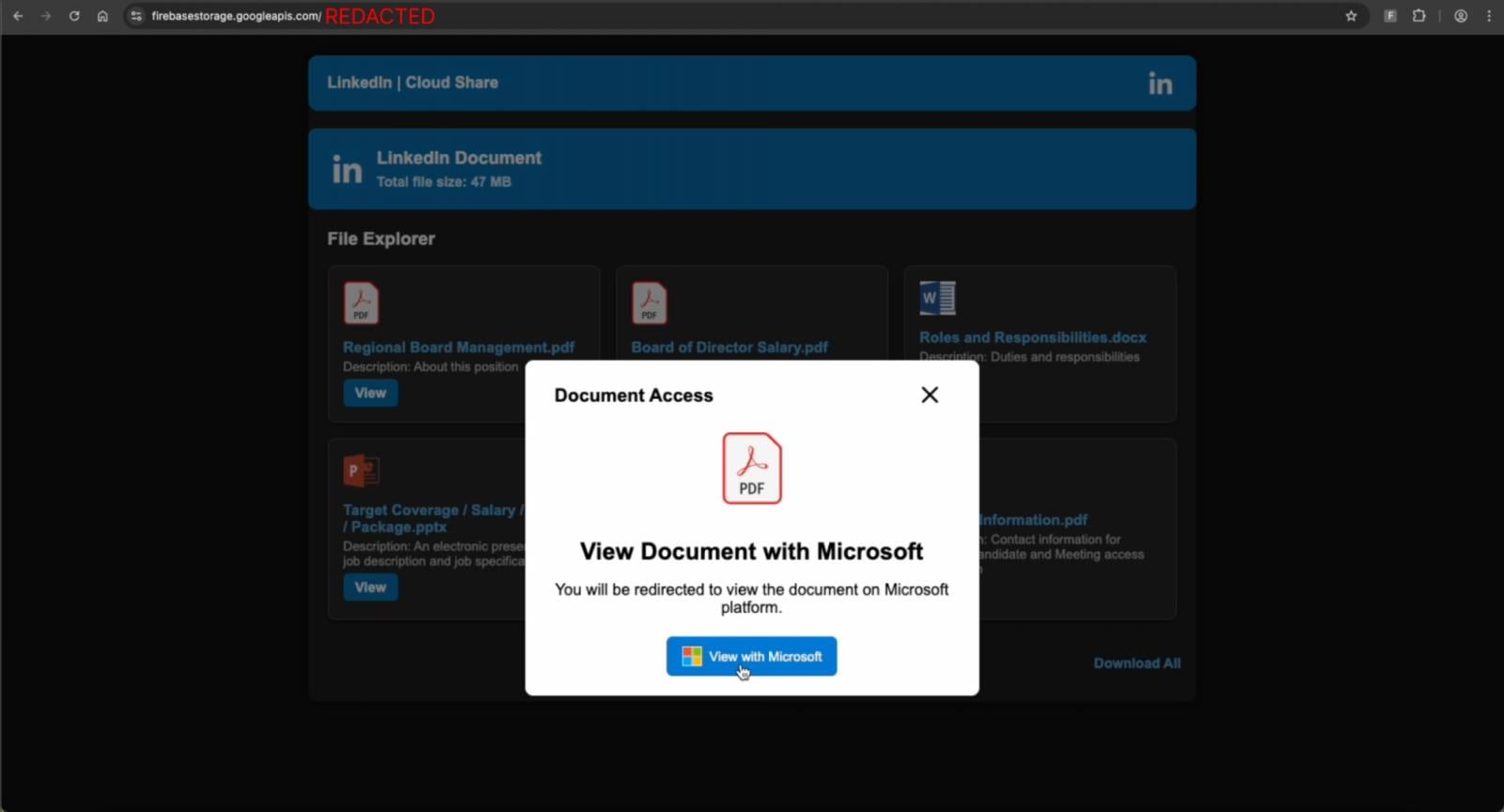
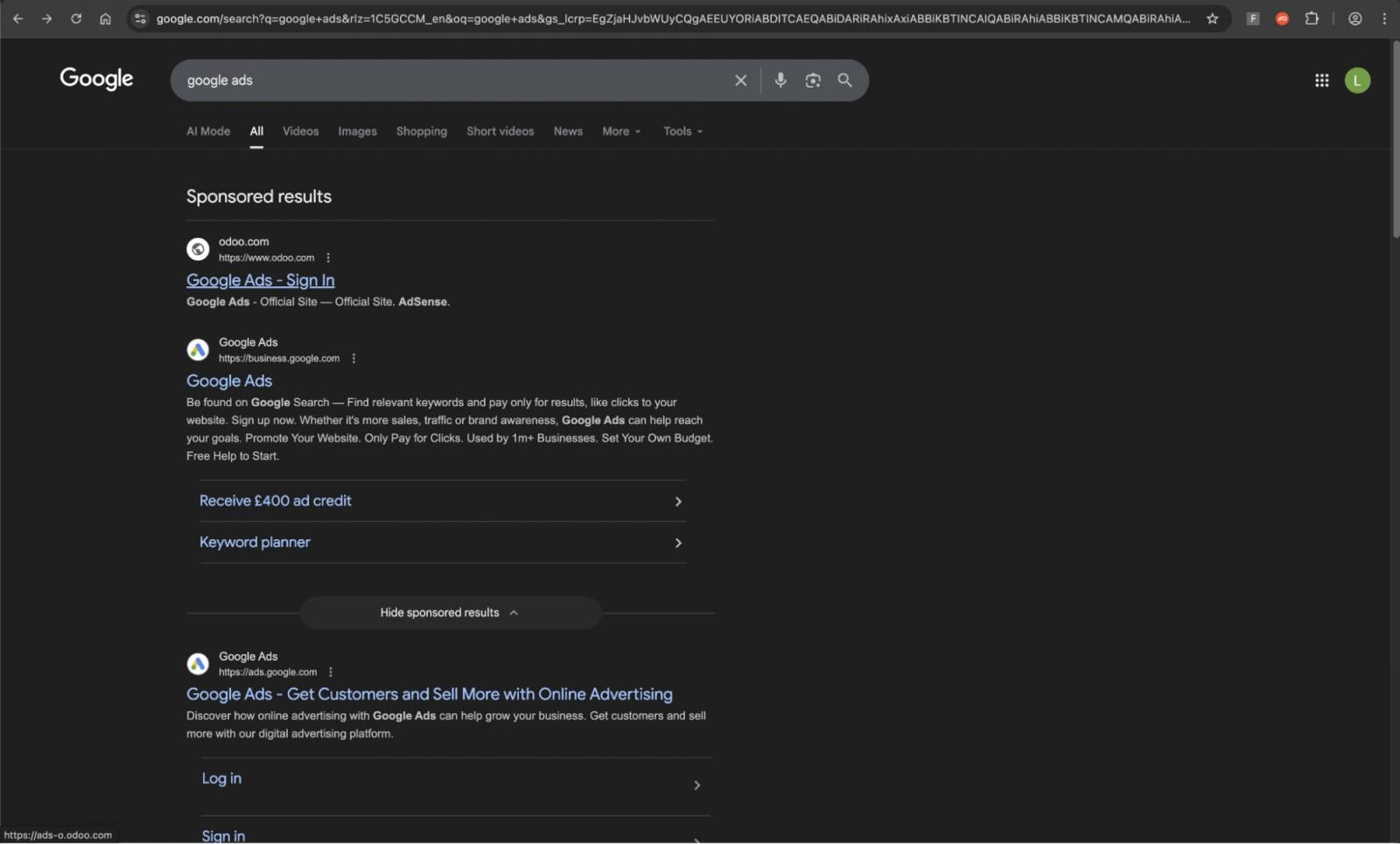
Phishing through non-email channels has a number of benefits. With e-mail being the very best protected phishing vector, it sidesteps these controls totally. There’s no must construct up your sender fame, discover methods to trick content material evaluation engines, or hope your message doesn’t find yourself within the spam folder.
As compared, non-email vectors have virtually no screening, your safety workforce has no visibility, and customers are much less prone to anticipate potential phishing.
It’s controversial that an organization Exec is extra prone to interact with a LinkedIn DM from a good account than a chilly e-mail. And social media apps do nothing to analyse messages for phishing hyperlinks. (And due to the restrictions of URL-based checks in relation to right this moment’s multi-stage phishing assaults, this could be extraordinarily troublesome even when they tried).
Serps additionally current an enormous alternative for attackers, whether or not they’re compromising current, excessive fame websites, spinning up malicious advertisements, or just vibe coding their very own Website positioning-optimised web sites.
That is an efficient approach to launch “watering gap” type assaults, casting a large web to reap credentials and account entry that may be re-sold to different criminals for a price, or leveraged by companions within the cybercriminal ecosystem as a part of main cyber breaches (such because the latest assaults by the “Scattered Lapsus$ Hunters” prison collective, all of which started with identity-based preliminary entry).
Take a look at the newest webinar from Push Safety on December seventeenth to learn the way phishing has developed in 2025, as Push researchers break down probably the most attention-grabbing assaults they’ve handled within the discipline, and what safety groups want to arrange for phishing in 2026.
#2: Legal PhaaS kits dominate
The overwhelming majority of phishing assaults right this moment use a reverse proxy. This implies they’re able to bypassing most types of MFA as a result of a session is created and stolen in actual time as a part of the assault. There isn’t a draw back to this strategy in comparison with the fundamental credential phishing that was the norm greater than a decade in the past.
These Attacker-in-the-Center assaults are powered by prison Phishing-as-a-Service (PhaaS) kits akin to Tycoon, NakedPages, Sneaky2FA, Flowerstorm, Salty2FA, together with numerous Evilginx variations (nominally a device for crimson teamers, however extensively utilized by attackers).
PhaaS kits are extremely essential to cybercrime as a result of they make subtle and repeatedly evolving capabilities accessible to the prison market, reducing the barrier to entry for criminals operating superior phishing campaigns.
This isn’t distinctive to phishing: Ransomware-as-a-Service, Credential Stuffing-as-a-Service, and lots of extra for-hire instruments and providers exist for criminals to make use of for a price.
This aggressive surroundings has fuelled attacker innovation, leading to an surroundings through which MFA-bypass is desk stakes, phishing-resistant authentication is being circumvented by means of downgrade assaults, and detection evasion methods are getting used to bypass safety instruments — from e-mail scanners, to web-crawling safety instruments, to internet proxies analyzing community site visitors.
It additionally signifies that when new capabilities emerge — akin to Browser-in-the-Browser — these are shortly built-in into a spread of phishing kits.
Among the most prevalent detection evasion strategies we’ve seen this 12 months are:
-
Widespread use of bot safety. Each phishing web page right this moment comes with both a customized CAPTCHA or Cloudflare Turnstile (reputable and faux variations) designed to dam web-crawling safety bots from with the ability to analyse phishing pages.
-
In depth redirect chains between the preliminary hyperlink seeded out to the sufferer, and the precise malicious web page internet hosting phishing content material, designed to bury phishing websites amongst a number of reputable pages.
-
Multi-stage web page loading carried out client-side through JavaScript. Because of this pages are conditionally loaded, and if situations aren’t met, malicious content material isn’t served — so the web page seems clear. This additionally signifies that a lot of the malicious exercise is going on regionally, with out creating internet requests that may be analysed by community site visitors evaluation instruments (e.g. internet proxies).
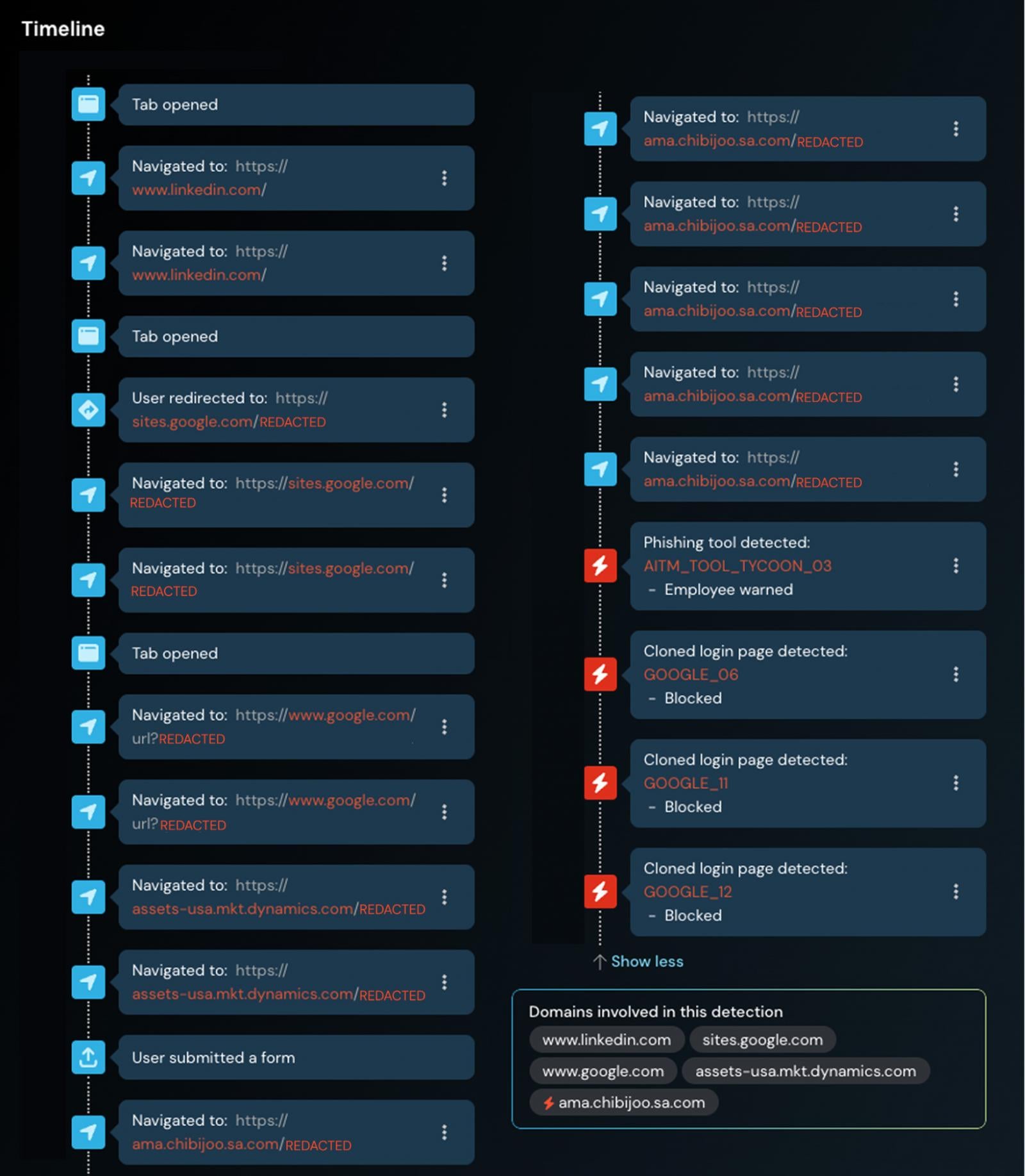
This contributes to an surroundings the place phishing goes undetected for prolonged intervals of time. Even when a web page is flagged, it’s trivial for attackers to dynamically serve up completely different phishing pages from the identical benign chain of URLs used within the assault.
That is all to say that the old-school strategy to URL blocking unhealthy websites is turning into a lot more durable and leaves you two steps behind attackers always.
#3: Attackers discover methods round phishing-resistant authentication (and different safety controls)
We already talked about that MFA downgrade has been an space of focus for safety researchers and attackers. However phishing-resistant authentication strategies (i.e. passkeys) stay efficient as long as the phishing-resistant issue is the one potential login issue, and there are not any backup strategies enabled for the account. (Although due to the logistical points of getting only one issue, that is pretty unusual.)
Equally, entry management insurance policies may be utilized on bigger enterprise apps and cloud platforms to scale back the chance of unauthorized entry (though these may be difficult to implement and preserve with out error).
In any case, attackers are contemplating all eventualities and searching for alternative routes into accounts which are much less nicely protected. This primarily includes attackers circumventing the usual authentication course of, by means of methods akin to:
-
Consent phishing: Tricking victims into connecting malicious OAuth apps into their app tenant.
-
Machine code phishing: The identical as consent phishing, however authorizing by means of the machine code move designed for machine logins that can’t help OAuth, by offering a substitute passcode.
-
Malicious browser extensions: Tricking victims into putting in a malicious extension (or hijacking an current one) to steal credentials and cookies from the browser.
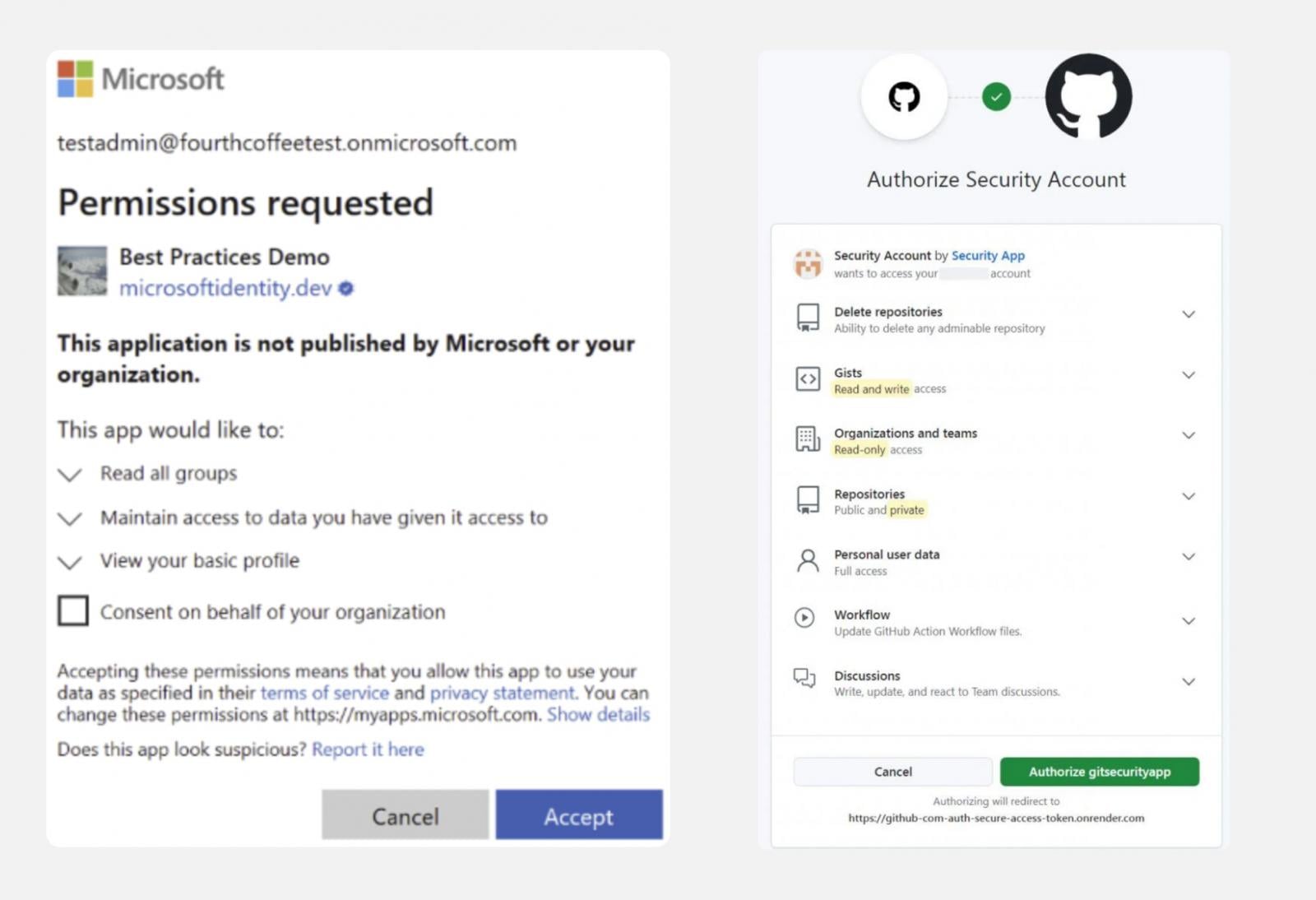
One other approach that attackers are utilizing to steal credentials and periods is ClickFix. ClickFix was the high preliminary entry vector detected by Microsoft final 12 months, concerned in 47% of assaults.
Whereas not a standard phishing assault, this sees attackers socially engineer customers into operating malicious code on their machine, usually deploying distant entry instruments and infostealer malware. Infostealers are then used to reap credentials and cookies for preliminary entry to numerous apps and providers.
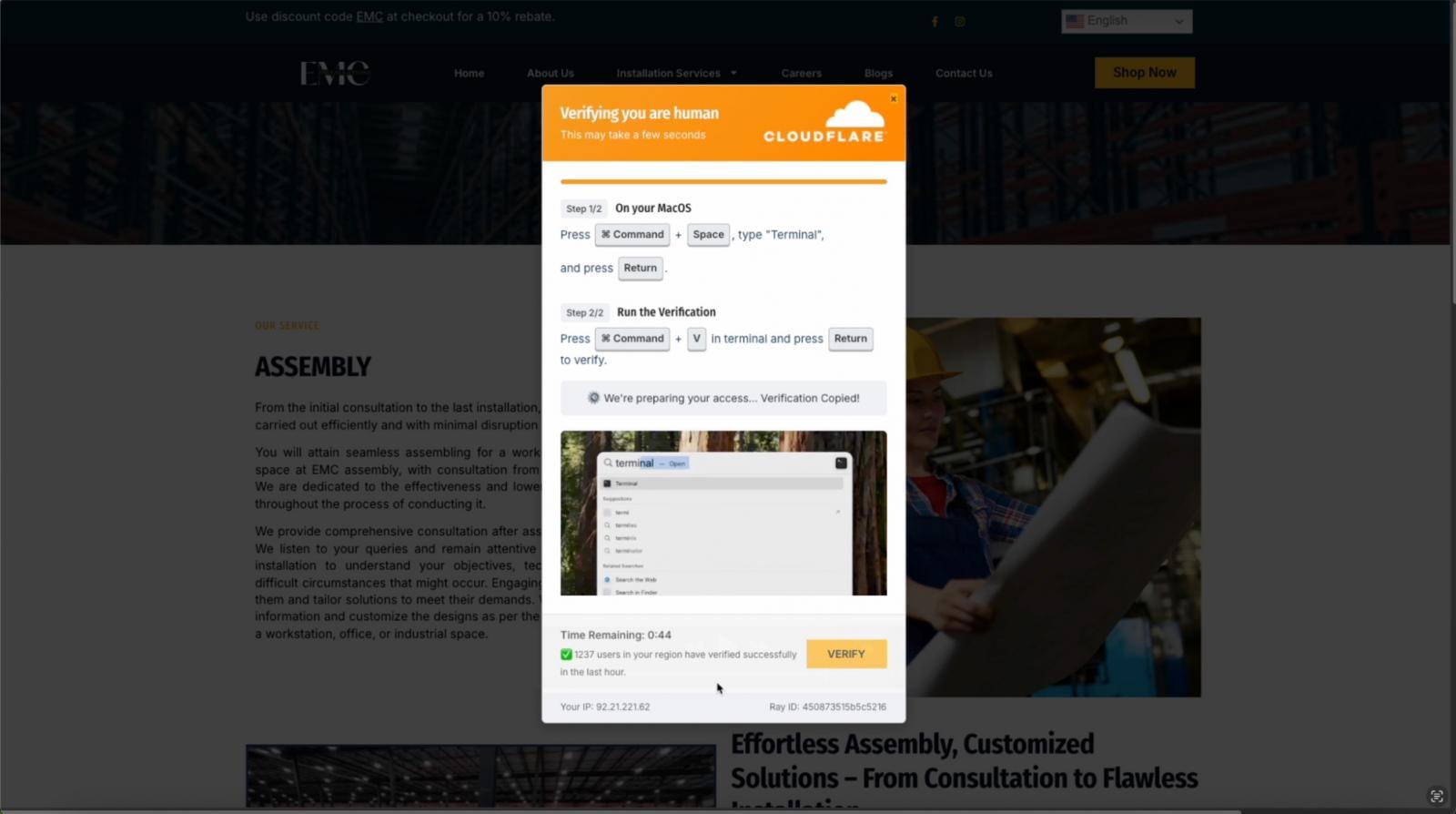
Push Safety researchers have additionally found a model new approach dubbed ConsentFix — a browser-native model of ClickFix that leads to an OAuth connection being established to the goal app, just by copying and pasting a reputable URL containing OAuth key materials.

That is much more harmful than ClickFix as it’s totally browser-native — eradicating the endpoint detection floor (and powerful safety controls like EDR) from the equation totally. And within the explicit case noticed by Push, the attackers focused Azure CLI — a first-party Microsoft app that has particular permissions and might’t be restricted like third-party apps.
Actually, there are many completely different methods attackers can use to take over accounts on key enterprise purposes — it’s outdated to think about phishing as being locked in to passwords, MFA, and the usual authentication move.
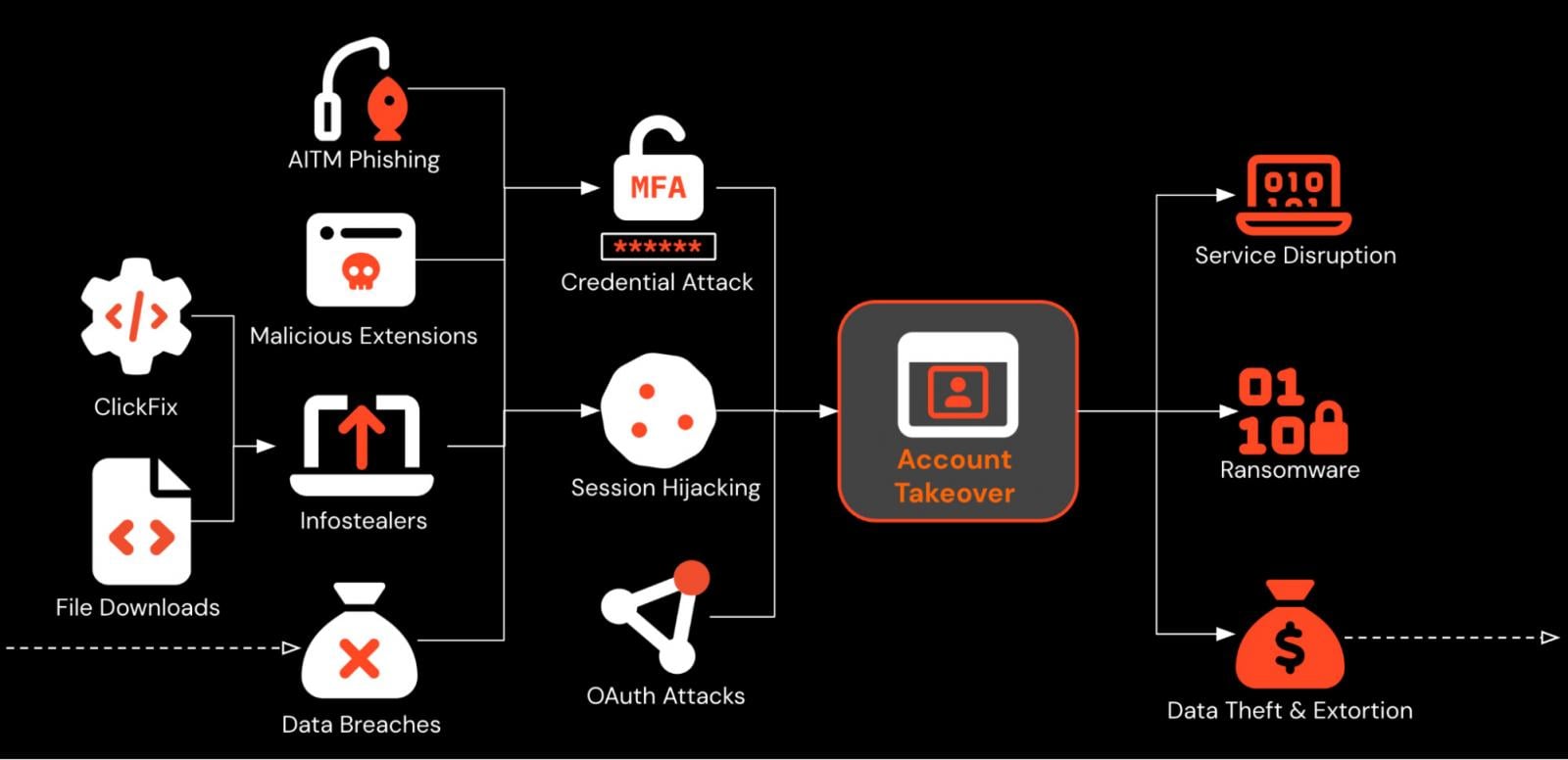
Steering for safety groups in 2026
To sort out phishing in 2026, safety groups want to vary their menace mannequin for phishing, and acknowledge that:
-
It’s not sufficient to guard e-mail as your predominant anti-phishing floor
-
Community and site visitors monitoring instruments aren’t maintaining with fashionable phishing pages
-
Phishing-resistant authentication, even when completely carried out, doesn’t make you immune
Detection and response is vital. However most organizations have vital visibility gaps.
Fixing the detection hole within the browser
One factor that these assaults have in widespread is that all of them happen within the internet browser, concentrating on customers as they go about their work on the web. That makes it the right place to detect and reply to those assaults. However proper now, the browser is a blind-spot for many safety groups.
Push Safety’s browser-based safety platform supplies complete detection and response capabilities towards the main explanation for breaches. Push blocks browser-based assaults like AiTM phishing, credential stuffing, malicious browser extensions, ClickFix, and session hijacking.
You don’t want to attend till all of it goes mistaken — you may as well use Push to proactively discover and repair vulnerabilities throughout the apps that your workers use, like ghost logins, SSO protection gaps, MFA gaps, weak passwords, and extra to harden your id assault floor.
To be taught extra about Push, take a look at our newest product overview or e book a while with certainly one of our workforce for a dwell demo.
Sponsored and written by Push Safety.

